Dakota Cary
Table of contents
Executive summary
China recognizes that many nondemocratic and illiberal developing nations need internet connectivity for economic development. These countries aim to digitize trade, government services, and social interactions, but interconnectivity risks better communication and coordination among political dissidents. China understands this problem and is trying to build global norms that facilitate the provision of its censorship and surveillance tools to other countries. This so-called Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace, is based around the idea of cyber sovereignty. China contends that it is a state’s right to protect its political system, determine what content is appropriate within its borders, create its own standards for cybersecurity, and govern access to the infrastructure of the internet.
Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace, a white paper from the government of the People’s Republic of China (most recently released in 2022 but reissued periodically since 2015), is a continuation of diplomatic efforts to rally the international community around China’s concept of cyber sovereignty.1 By extending the concept of sovereignty to cyberspace, China makes the argument that the state decides the content, operations, and norms of its internet; that each state is entitled to such determinations as a de facto right of its existence; that all states should have equal say in the administration of the global internet; and that it is the role of the state to balance claims of citizens and the international community (businesses, mostly, but also other states and governing bodies).
But making the world safe for authoritarian governments is only part of China’s motivation. As the key provider of censorship-ready internet equipment and surveillance tools, China’s concept of cyber sovereignty offers political security to other illiberal governments. Case studies in this report demonstrate how such technologies may play a role in keeping China’s friends in power.
The PRC supports other authoritarian governments for good reason. Many countries in which Chinese state-owned enterprises and PRC-based companies own mineral drawing rights or have significant investments are governed by authoritarians. Political instability threatens these investments, and, in some cases, China’s access to critical mineral inputs to its high-tech manufacturing sector. Without a globally capable navy to compel governments to keep their word on contracts, China is at the mercy of democratic revolutions and elite power struggles in these countries. By providing political security to a state through censorship, surveillance, and hacking of dissidents, China improves its chances of maintaining access to strategic plots of land for military bases or critical manufacturing inputs. A government that perceives itself to be dependent on China for political security is in no position to oppose it.
Outside of China’s strategic objectives, the push for a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace may also have an operational impact on state-backed hacking teams.
As China’s cybersecurity companies earn more customers, their defenders gain access to more endpoints, better telemetry, and a more complete view of global cyber events. Leveraged appropriately, a larger customer base improves defenses. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology’s Cybersecurity Threat and Vulnerability Information Sharing Platform, which collects information about software vulnerabilities, also collects voluntary incident response reports from Chinese firms responding to breaches of their customers.2 Disclosure of incidents and the vulnerabilities of overseas clients of Chinese cybersecurity firms would significantly increase the PRC’s visibility into global cyber operations by other nations or transnational criminal groups. China’s own defensive posture should also improve as its companies attract more global clients.
China’s offensive teams could benefit, too. Many cybersecurity firms often allow their own country’s security services to operate unimpeded in their customers’ networks.3 Therefore, it is likely that more companies protected by Chinese cybersecurity companies means fewer networks where China’s offensive hacking teams must worry about evading defenses.
This report uses cases studies from the Solomon Islands, Russia, and beyond to show how China is operationalizing its view of cyber sovereignty.
Introduction
A long black slate wall covered in dark hexagonal tiles runs along the side of Nuhong Street in Wuzhen, China, eighty miles southwest of Shanghai. A gap in the middle of the wall leads visitors to the entrance of the Waterside Resort that, for the last nine years, has hosted China’s World Internet Conference, a premier event for Chinese Communist Party (CCP) cyber policymakers.
The inaugural conference didn’t seem like a foreign policy forum. The thousand or so attendees from a handful of countries and dozens of companies listened to a speaker circuit asserting that 5G is the future, big data was changing the world, and the internet was great for economic development—hardly groundbreaking topics in 2014.4 But the internet conference was more than a platform for platitudes about the internet: it also served as China’s soft launch for its international strategy on internet governance.
By the last evening of the conference, some of the attendees had already left, choosing the red-eye flight home over another night by the glass-encased pool on the waterfront. Around 11 p.m., papers slid under doorways up and down the hotel halls. Conference organizers went room by room distributing a proclamation they hoped attendees would endorse just nine hours later.5 Attendees were stunned. The document said: “During the conference, many speakers and participants suggest [sic] that a Wuzhen declaration be released at the closing ceremony.” The papers, stapled and stuffed under doors, outlined Beijing’s views of the internet. The conference attendees—many of whom were members of the China-friendly Shanghai Cooperation Organization—balked at the last-minute, tone-deaf approach to getting an endorsement of Beijing’s thoughts on the internet. The document went unsigned, and the inaugural Wuzhen internet conference wrapped without a sweeping declaration. It was clear China needed the big guns, and perhaps less shady diplomatic tactics, to persuade foreigners of the merits of their views of the internet.
President Xi Jinping headlined China’s second World Internet Conference in 2015.6 This time the organizers skipped the late-night antics. On stage and reportedly in front of representatives from more than 120 countries and many more technology firm CEOs, Xi outlined a vision that is now enshrined in text as “Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace.”7 The four principles and five proposals President Xi laid out in his speech, which generally increase the power of the state and aim to model the global internet in China’s image, remain a constant theme in China’s diplomatic strategy on internet governance.8 In doing so, Xi fired the starting gun on an era of global technology competition that may well lead to blocs of countries aligned by shared censorship and cybersecurity standards. China has reissued the document many times since Xi’s speech, with the latest coming in 2022.
Xi’s 2015 speech came at a pivotal moment in history for China and many other authoritarian regimes. The Arab Spring shook authoritarian governments around the world just years earlier.9 Social media-fueled revolutions saw some autocrats overthrown or civil wars started in just a few months. China shared the autocrats’ paranoia. A think tank under the purview of the Cyberspace Administration of China acutely summarized the issue of internet governance, stating: “If our party cannot traverse the hurdle represented by the Internet, it cannot traverse the hurdle of remaining in power for the long term.”10 Another PRC government agency report went even further: blaming the US Central Intelligence Agency for no fewer than eleven “color revolutions” since 2003: the National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center claimed that the United States was providing critical technical support to pro-democracy protestors.11 Specifically, the center blamed the CIA for five technologies—ranging from encrypted communications to “anti-jamming” WiFi that helped connect protestors—that played into the success of color revolutions. Exuberance in Washington over the internet leveling the playing field between dictators and their oppressed citizens was matched in conviction, if not in tone, by leaders from Beijing to Islamabad.
But China and other repressive regimes could not eschew the internet. The internet was digitizing everything, from social relationships and political affiliations to commerce and trade. Authoritarians needed a way to reap the benefits of the digital economy without introducing unacceptable risks to their political systems. China’s approach, called a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace,12 responds to these threats as a call to action for authoritarian governments and a path toward more amenable global internet governance for authoritarian regimes. It is, as one expert put it, China switching from defense to offense.13
The core of China’s approach
The PRC considers four principles key to structuring the future of cyberspace. These principles lay the conceptual groundwork for the five proposals, which reflect the collective tasks to build this new system. Table 1 shows the principles, which were drawn from Xi’s 2015 speech.14
Table 1: China’s Four Principles, in Xi’s Words
- Respect for cyber sovereignty: “The principle of sovereign equality enshrined in the Charter of the United Nations is one of the basic norms in contemporary international relations. It covers all aspects of state-to-state relations, which also includes cyberspace. We should respect the right of individual countries to independently choose their own path of cyber development, model of cyber regulation and Internet public policies, and participate in international cyberspace governance on an equal footing. No country should pursue cyber hegemony, interfere in other countries’ internal affairs or engage in, connive at or support cyber activities that undermine other countries’ national security.”
- Maintenance of peace and security: “A secure, stable and prosperous cyberspace is of great significance to all countries and the world. In the real world, there are still lingering wars, shadows of terrorism and occurrences of crimes. Cyberspace should not become a battlefield for countries to wrestle with one another, still less should it become a hotbed for crimes. Countries should work together to prevent and oppose the use of cyberspace for criminal activities such as terrorism, pornography, drug trafficking, money laundering and gambling. All cyber crimes, be they commercial cyber thefts or hacker attacks against government networks, should be firmly combated in accordance with relevant laws and international conventions. No double standards should be allowed in upholding cyber security. We cannot just have the security of one or some countries while leaving the rest insecure, still less should one seek the so-called absolute security of itself at the expense of the security of others.”
- Promotion of openness and cooperation: “As an old Chinese saying goes, ‘When there is mutual care, the world will be in peace; when there is mutual hatred, the world will be in chaos.’ To improve the global Internet governance system and maintain the order of cyberspace, we should firmly follow the concept of mutual support, mutual trust and mutual benefit and reject the old mentality of zero-sum game or ‘winner takes all.’ All countries should advance opening-up and cooperation in cyberspace and further substantiate and enhance the opening-up efforts. We should also build more platforms for communication and cooperation and create more converging points of interests, growth areas for cooperation and new highlights for win-win outcomes. Efforts should be made to advance complementarity of strengths and common development of all countries in cyberspace so that more countries and people will ride on the fast train of the information age and share the benefits of Internet development.”
- Cultivation of good order: “Like in the real world, freedom and order are both necessary in cyberspace. Freedom is what order is meant for and order is the guarantee for freedom. We should respect Internet users’ rights to exchange their ideas and express their minds, and we should also build a good order in cyberspace in accordance with law as it will help protect the legitimate rights and interests of all Internet users. Cyberspace is not a place beyond the rule of law. Cyberspace is virtual, but players in cyberspace are real. Everyone should abide by the law, with the rights and obligations of parties concerned clearly defined. Cyberspace must be governed, operated and used in accordance with law, so that the Internet can enjoy sound development under the rule of law. In the meantime, greater efforts should be made to strengthen ethical standards and civilized behaviors in cyberspace. We should give full play to the role of moral teachings in guiding the use of the Internet to make sure that the fine accomplishments of human civilizations will nourish the growth of cyberspace and help rehabilitate cyber ecology.”
The four principles are not of equal importance. “Respecting cyber sovereignty” is the cornerstone of China’s vision for global cyber governance. China introduced and argued for the concept in its first internet white paper in 2010.15 But cyber sovereignty is not itself controversial. The idea that a government can regulate things within its borders is nearly synonymous with what it means to be a state. Issues arise with the prescriptive and hypocritical nature of the three following principles.
Under the “maintenance of peace and security principle,” China—a country with a famously effective and persistent ability to steal and commercialize foreign intellectual property16—suggests that all countries should abhor cyberattacks that lead to IP theft or government spying. Xi’s statement establishes equivalency between two things held separate in Western capitalist societies: intellectual property rights and trade secrets versus espionage against other governments. China holds what the US prizes but cannot defend well, IP and trade secrets, next to what China prizes but cannot guarantee for itself, the confidentiality of state secrets. The juxtaposition was an implicit bargain and one that neither would accept. In considering China’s proposition, the US continuation of traditional intelligence-collection activities contravenes China’s “peace and security principle,” providing the Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson a reason to blame the United States when China is caught conducting economic espionage.
“Promotion of openness and cooperation” is mundane enough to garner support until users read the fine print or ask China to act on this principle. Asking other countries to throw off a zero-sum mentality and view the internet as a place for mutual benefit, Xi unironically asks states to pursue win-win benefits. This argument blatantly ignores the clear differences in market access between foreign tech companies in the PRC and Chinese firms’ access to foreign markets. Of course, if a country allows a foreign firm into its market, by Xi’s argumentation, the country must have decided it was a win-win decision. It’s unclear if refusing market access to a Chinese company would be acceptable or if that would fall under zero-sum mentality and contravene the value of openness. Again, China’s rhetoric misrepresents the conditions it would likely accept.
Cultivating “good order” in cyberspace, at least as Xi conceptualizes it, is impossible for democratic countries with freedom of speech. Entreaties that “order” be the guarantor of freedom of speech won’t pass muster in many nations, at least not the “order” sought by China’s policymakers. A report from the Institute for a Community with a Shared Future shines light onto what type of content might upset the “good order.” In its Governing the Phenomenon of Online Violence Report, analysts identify political scandals like a deadly 2018 bus crush in Chongqing or the 2020 “Wuhan virus leak rumor” as examples of online violence, alongside a case where a woman was bullied to suicide.17 Viewing political issues as “online violence” associated with good order is not just a one-off report. Staff at the Institute argue that rumors spread at the start of the pandemic in 2020 “highlight the necessity and urgency of building a community with a shared future in cyberspace.”18 For China, “online violence” is a euphemism for speech deemed politically sensitive by the government. If “making [the internet] better, cleaner and safer is the common responsibility of the international community,”19 as Xi argues, how will China treat countries it sees as abrogating its responsibility to combat such online violence? Will countries whose internet service providers rely on Chinese cloud companies or network devices be able to decide that criticizing China is acceptable within its own borders?
China’s five proposals
The five proposals used to construct China’s Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace carry less weight and importance than its four principles. The proposals are not apparently attached to specific funding or policy initiatives, and did not receive attention from China’s foreign ministry. They are, at most, way stations along the path to a shared future. The proposals are:
- Speeding up the construction of a global internet infrastructure and promoting interconnectivity.
- Building an online platform for cultural exchange and mutual learning.
- Promoting the innovative development of the cyber economy and common prosperity.
- Maintaining cyber security and promoting orderly development.
- Building an internet governance system and promoting equity and justice.
Implications and the future of the global internet
China’s argument for its view of global internet governance and the role of the state rests on solid ground. The PRC frequently points to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union as a leading example of the state’s role in internet regulation. The GDPR allows EU citizens to have their data deleted, forces businesses to disclose data breaches, and requires websites to give users a choice to accept or reject cookies (and what kind) each time they visit a new website. China points to concerns in the United States over foreign interference on social media as evidence of US buy-in on China’s view of cyber sovereignty. Even banal regulations like the US “know your customer” rule—which requires some businesses to collect identifying personal information about users, usually for tax purposes—fit into Beijing’s bucket of evidence. But the alleged convergence between the views of China and democratic nations stops there.
Divergent values between liberal democracies and the coterie of PRC-aligned autocracies belie our very different interpretations of the meaning of cyber sovereignty. A paper published in the CCP’s top theoretical journal mentions both the need to regulate internet content and “promote positive energy,” a Paltrowesque euphemism for party-boosting propaganda, alongside
endorsements of the cyber sovereignty principle.20 The article extrapolates on what Xi made clear in his 2015 speech. For the CCP, censorship and sovereignty are inextricably linked.
These differences are not new. Experts dedicate significant coverage to ongoing policy arguments at the UN, where China repeatedly pushes to classify the dissemination of unwanted content—read politically intolerable—as a crime.21 As recently as January 2023, China offered an amendment to a UN treaty attempting to make sharing false information online illegal.22 A knock-on effect of media coverage related to disinformation campaigns from China and Russia—despite their poor performance23—means policymakers, pundits, and journalists make China’s point that narratives promoted by other nations is an issue to be solved. What counts as disinformation can be meted out on a country-by-country basis. The tension between the desire to protect democracy from foreign influence and the liberal value of promoting free speech and truth in authoritarian systems is palpable.
The United States has fueled the CCP’s concern with its public statements. China’s internet regulators criticized the United States’ Declaration for the Future of the Internet.24 The CCP, which is paranoid about foreign attempts to support “color revolutions” or foment regime change, is rightfully concerned. The United States’ second stated principle for digital technologies is to promote “democracy,” a value antithetical to continuing CCP rule over the PRC. The universal value democratic governments subscribe to—the consent of the governed—drives the US position on the benefits of connectedness. That same value scares authoritarian governments.
Operationalizing our shared future
Jointly Build a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace alludes to the pathways the CCP will use to act on its vision. The document includes detailed statistics about the rollout of IPv6—a protocol for issuing internet-connected device addresses that could ease surveillance—use of the Beidou Satellite Navigation system within China and elsewhere, the domestic and international use of 5G, development of transformational technologies like artificial intelligence and Internet of Things devices, and the increasingly widespread use of internet-connected industrial devices.25 The value of different markets, like that of e-commerce or trade enabled by any of the preceding systems, are repeated many times over the course of the document. It’s clear that policymakers see the fabric of the internet—its devices, markets, and economic value—as expanding. Owning the avenues of expansion, then, is key to spreading the CCP’s values as much as it is about making money.
Authoritarian and nondemocratic developing countries provide a bountiful market for China’s goods. Plenty of developing nations and authoritarian governments want to tighten control over the internet in their countries. Recent research demonstrates an increasing number of incidents when governments shut off the internet in their countries—a good proxy for their interest in censorship.26 These governments need the technology and tools to finely tune their control over the internet. Owing to the political environment inside the PRC, Chinese tech firms already build their products to facilitate censorship and surveillance.27 Some countries are having luck rolling out these services. The Australian Strategic Policy Institute found that “with technical support from China, local governments in East Africa are escalating censorship on social media platforms and the internet.”28 These findings are mirrored by reporting from Censys, a network data company, that found, among other things, a significant footprint for PRC-made network equipment in four African countries.29 In fact, there is no public list of countries that acknowledge supporting the Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace approach, but there are good indicators for which nations are mostly likely to participate.
A 2017 policy paper entitled International Strategy of Cooperation on Cyberspace indicated that China would carry out “cybersecurity cooperation” with “the Conference on Interaction and Confidence Building Measures in Asia (CICA), Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), China-Arab States Cooperation Forum, Forum of China and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States and Asian-African Legal Consultative Organization.”30 But an international strategy document stating the intent to cooperate with most of the Global South is not the same as actually doing so. The 2017 strategy document is, at most, aspirational.
Instead, bilateral agreements and technical agreements between government agencies to work together on cybersecurity or internet governance are better indicators of who is part of China’s “community with a shared future.” For example, Cuba and the PRC signed a comprehensive partnership agreement on cybersecurity in early 2023, though the content of the deal remains secret.31 China has made few public announcements about other such agreements. In their place, the China National Computer Emergency Response Center (CNCERT) has “established partnerships with 274 CERTs in 81 countries and territories and signed cybersecurity cooperation memorandums with 33 of them.”32 But even these countries are not publicly identified.33 A few nations or groups are regularly mentioned around the claims of CNCERT’s international partnerships, however. Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Brazil, South Africa, Benin, and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization are frequently mentioned. The paper on jointly building a community also mentions the establishment of the China-ASEAN Cybersecurity Exchange and Training Center, the utility of which may be questioned given China’s track record of state-backed hacking campaigns against its members.34
Along with the identity of their signatories, the contents of these agreements and their benefits also remain private. Without access to any of these agreements, one can only speculate about their benefits. There are also no countries especially competent at cyber operations or cybersecurity mentioned in the list above. The result may be that CNCERT and its certified private-sector partners receive “first dibs” when government agencies or other entities in these countries need incident response services; receiving favorable terms or financing from the Export-Import Bank of China to facilitate the purchase of PRC tech also aligns with other observed behavior.35
Besides favorable terms of trade for PRC tech and cybersecurity firms, some of the CNCERT international partners may also be subject to intelligence-sharing agreements. CNCERT operates a software vulnerability database called China National Information Security Vulnerability Sharing Platform, which accepts submissions from the public and partners with at least three other vulnerability databases.36 CNCERT’s international partnerships could add another valuable pipeline of software vulnerability information into China’s ecosystem. Moreover, under a 2021 regulation, Chinese firms conducting incident response for clients can voluntarily disclose those incidents to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology’s “Cybersecurity Threat and Vulnerability Information Sharing Platform,” which has a separate system for collecting information about breaches.37 The voluntary disclosure of incidents and mandatory disclosure of vulnerabilities observed in overseas clients of Chinese cybersecurity firms would significantly increase the PRC’s visibility into global cyber operations by other nations or transnational criminal groups.
Offensive capabilities, not just global cybersecurity, might be on CCP policymakers’ minds, too, when other countries agree to partner with China. Cybersecurity firms frequently allow their own country’s offensive teams to work unimpeded on their customers’ networks: with each new client China’s cybersecurity companies add to their rosters, China’s state-backed hackers may well gain another network where they can work without worrying about defenders.38 In this vein, Chen Yixin, the head of the Ministry of State Security, attended a July 2023 meeting of the Cyberspace Administration of China that underlined the importance of the Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace.39 In September 2023, Chen published commentary in the magazine of the Cyberspace Administration of China arguing that supporting the Shared Future in Cyberspace was important work.40 Researchers from one cybersecurity firm found that the PRC has been conducting persistent, offensive operations against many African and Latin American states, even launching a special cross-industry working group to monitor PRC activities in the Global South.41 Chinese cybersecurity companies operating in those markets have not drawn similar attention to those operations.
But China’s network devices and cybersecurity companies don’t just facilitate surveillance, collect data for better defense, or offer a potential offensive advantage, they can also be used to shore up relationships between governments and provide Beijing an avenue for influence. The Wall Street Journal exposed how Huawei technicians were involved in helping Ugandan security services track political opponents of the government.42 China’s government and its companies support such operations elsewhere, too. One source alleged that PRC intelligence officers were involved in cybersecurity programs of the UAE government, including offensive hacking and collection for the security services.43 The closeness of the relationship is apparent in other ways, too. The UAE is reportedly allowing China’s military to build a naval facility, jeopardizing the longevity of US facilities in the area, and tarnishing the UAE’s relationship with the United States.44
Providing other nondemocratic governments with offensive services and capabilities allows China to form close relationships with other regimes whose primary goal, like the CCP, is to maintain the current government’s hold on power. In illiberal democracies, such cooperation helps Beijing expand its influence and provides backsliding governments capabilities they would not otherwise have.
China is plainly invested in the success of many other nondemocratic governments. Around the world, state-owned enterprises and private companies have inked deals in extractive industries that total billions of dollars. Many of these deals, say for mining copper or rare earth elements, provide critical inputs to China’s manufacturing capacity—they are the lifeblood of many industries, from batteries to semiconductors.45 In countries without strong rule of law, continued access to mining rights may depend on the governments that signed and approved those operations staying in power. China is already suffering from such abrogation of agreements in Mexico after the country’s president renationalized the country’s lithium deposits.46 Countries where China has significant interests, like the Democratic Republic of the Congo, are also considering nationalizing such assets.47 Close relationships with political elites, bolstered by agreements that provide political security, make it more difficult for those elites to renege on their contracts—or lose power to someone else who might.
China cannot currently project military power around the world to enforce contracts or compel other governments. In lieu of a blue-water navy, China offers what essentially amounts to political security services by censoring internet content, monitoring dissidents, and hacking political opponents—and a way to align the interests of other authoritarian governments with its own. If a political leader feels that China is a guarantor of their own rule, they are much more likely to side with Beijing on matters big and small. A recent series of events in the Solomon Islands provide a portrait of what this can look like.
Case studies in China’s “shared future”
The saga surrounding the Solomon Islands provides a good example of China’s model for internet governance and the reasons for its adoption.
Over the course of 2022, the international community watched as the Solomon Islands vacillated on its course and in statements, and prevaricated about secret commitments to build a naval base for China. After a draft agreement for the Solomon Islands to host the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN), the navy of the CCP’s military, was leaked to the press in March 2022, representatives of the Solomon Islands stated the agreement would not allow PLA military bases.48 Senior delegations from both Australia and the United States rushed to meet with representatives of the Pacific Island nation.49 Even opposition leaders in the Solomon Islands—who were surprised by the leaked documents—agreed that claims of PLA military bases should not be taken at face value.50 The back and forth by the Solomon Islands’ political parties worried China. In May 2022, a Chinese hacking team breached the Solomon Islands’ government systems, likely to assess the future of their agreement in the face of the island nation’s denials.51
But the denials only bought Solomon Islands Prime Minister Manasseh Sogavare more time. In August, the ruling party introduced a bill to delay elections from May 2023 to December of that year.52 Shortly thereafter, the Solomon Islands announced a deal to purchase 161 Huawei telecoms towers financed by the Export-Import Bank of China.53 (The deal came just four years after Australia had successfully prevented the Solomon Islands from partnering with Huawei to lay undersea cables to provide internet access to the island nation.)54 Months later, the foreign press reported in October 2022 that the Solomon Islands had sent police to China for training.55 Local contacts in the security services may be useful for the PRC. A provision of the drafted deal leaked in March 2022 allows PLA service members to travel off base in the event of “social unrest.”56 Such contacts could facilitate interventions in a political crisis on behalf of PM Sogavare or his successor. In the summer of 2023, China and the Solomon Islands signed an agreement expanding cooperation on cybersecurity and policing.57
To recap, in a single year the Solomon Islands agreed to host a PLAN base, delayed an election for Beijing’s friend, sent security services to train in the PRC, and rolled out PRC-made telecommunications equipment that can facilitate surveillance of political opponents. In the international system the CCP seeks, one that makes normal the censorship of political opponents and makes it a crime to disseminate information critical of authoritarian regimes, the sale of censorship as a service directly translates into the power to influence domestic politics in other nations. If there was a case study to sell China’s version of internet governance to nascent authoritarian regimes around the world, it would be the Solomon Islands.
For countries with established authoritarian regimes, buying into China’s vision of internet governance and control is less about delaying elections and buying Huawei cell towers, and more about the transfer of expertise and knowledge of how to repress more effectively. Already convinced on the merits of China’s vision, these governments lack the expertise and technical capabilities to implement their shared vision of control over the internet.
Despite its capable but sometimes blunder-prone intelligence services, Russia was recently found to be soliciting technical expertise and training from China on how to better control its domestic internet content.58Documents obtained by Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty detailed how Russian government officials met with teams from the Cyberspace Administration of China in 2017 and 2019 to discuss how to crack down on virtual private networks, messaging apps, and online content. Russian officials even went so far as to request that a Russian team visit China to better understand how China’s Great Firewall works and how to “form a positive image” of Russia on the domestic and foreign internet.59 The leaked documents align with what the PRC’s policy document details already.
Since 2016, they have co-hosted five China-Russia Internet Media Forum[s] to strengthen new media exchanges and cooperation between the two sides. Through the Sino-Russian Information Security Consultation Mechanism, they have constantly enhanced their coordination and cooperation on information security.
The two countries formalized the agreement that served as the basis for their cooperation on the sidelines of the World Internet Conference in 2019.60 They could not have picked a better venue to signify what China’s Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace policy would mean for the world.
The Solomon Islands and Russia neatly capture the spectrum of countries that might be most interested in China’s vision for the global internet. At each step along the spectrum, China has technical capabilities, software, services, and training it can offer to regimes from Borneo to Benin.
In conclusion, the chart below provides a visualization of the spectrum of countries that could be the most interested in implementing China’s Community for a Shared Future in Cyberspace.61
Figure 1: PRC tech influence vs. democracy index score
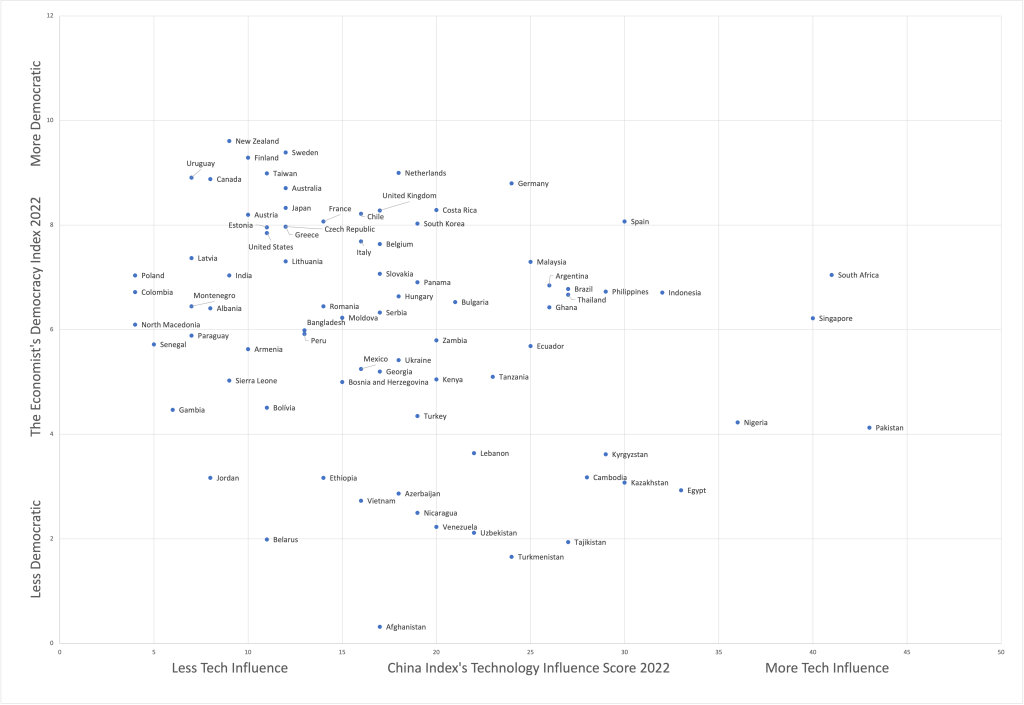
Sources: Data from “China Index 2022: Measuring PRC Influence Around the Globe,” Doublethink Lab and China In The World Lab, https://china-index.io/; and “The World’s Most, and Least, Democratic Countries in 2022,” Economist, February 1, 2023, https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2023/02/01/the-worlds-most-and-least-democratic-countries-in-2022.
By combining data from The Economist Democracy Index (a proxy for a country’s adherence to democratic norms and institutions) and Doublethink Lab’s China Index for PRC Technology Influence (limited to eighty countries and a proxy for a country’s exposure to, and integration of, PRC technology in its networks and services), this chart represents countries with low scores on democracy and significant PRC technology influence in the bottom right. Based on this chart, Pakistan in the most likely to support the Shared Future concept. Indeed, Pakistan has its own research center on the “Community for a Shared Future” concept.62The research center is hosted by the Communications University of China, which works closely with the CCP’s International Liaison Department responsible for keeping good relationships with foreign political parties.
Internet conference goes prime time
The 2022 Wuzhen World Internet Conference got an upgrade and name change: the annual conference became an organization based in Beijing and the summit continues as its event, now called the World Internet Conference (WIC). The content from all previous Wuzhen conferences plasters the new organization’s website.63
An odd collection of six entities founded the new WIC organization: Groupe Speciale Mobile Association (GSMA), a mobile device industry organization; China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC), which is responsible for China’s top-level .cn domain and IPv6 rollout, among others functions; ChinaCERT, mentioned above; Alibaba; Tencent; and Zhejiang Labs.64 Another report by the author connects the last organization, Zhejiang Labs, to research on AI for cybersecurity and some oversight by members of the PLA defense establishment.65
Though the Wuzhen iteration of the conference also included components of competition for technical innovation and research, the new collection of organizations overseeing WIC suggests it will focus more on promoting the fabric of the internet—hardware, software, and services—made by PRC firms. China’s largest tech companies including Alibaba and Tencent stand to benefit from China’s vision for global internet governance if the PRC can convince other countries to support its aims (and choose PRC firms to host their data in the process). Any policy changes tied to the elevation of the conference will become apparent over the coming years. For now, WIC will maintain the mission and goals of the Wuzhen conference.
Conclusion
China’s vision for the internet is really a vision for global norms around political speech, political oppression, and the proliferation of tools and capabilities that facilitate surveillance. Publications written by current and former PRC government officials on China’s “Shared Future for Humanity in Cyberspace” argue that the role of the state has been ignored until now, that each state can determine what is allowed on its internet—through the idea of cyber sovereignty, and that the political interests of the state are the core value that drives decision-making. Dressed up in language about the future of humanity, China’s vision for the internet is one safe for authoritarians to extract value from the interconnectedness of today’s economy while limiting risk to their regime’s stability.
China is likely to pursue agreements on cybersecurity and internet content control in regimes where it stands to lose most if the government changed hands. China’s grip on the critical minerals market is only as strong as its partners’ grip on power. In many authoritarian, resource-rich countries, a change of government could mean the renegotiation of contracts for access to natural resources or their outright nationalization—jeopardizing China’s access to important industrial inputs. Although internet censorship and domestic surveillance capabilities do not guarantee an authoritarian government will stay in power, it does improve their odds. China lacks a globally capable navy to project power and enforce contracts negotiated with former governments, so keeping current signatories in power is China’s best bet.
China will not have to work hard to promote its vision for internet governance in much of the world. Instead of China advocating for a new system that countries agree to use, then implement, the causality is reversed. Authoritarian regimes that seek economic benefits of widespread internet access are more apt to deploy PRC-made systems that facilitate mass surveillance, thus reducing the risks posed by increased connectivity. China’s tech companies are well-positioned to sell these goods, as their domestic market has forced them to perfect the capabilities of oppression.66 The example of Russia’s cooperation and learning from China demonstrates what the demand signal from other countries might look like. Elsewhere, secret agreements between national CERTs could facilitate access that allows for greater intelligence collection and visibility. Many Arabian Gulf countries already deploy PRC-made telecoms kit and hire PRC cybersecurity firms to do sensitive work. As the world’s autocrats roll out China’s technology, their countries will be added to the brochures of firms advertising internet connectivity, surveillance, and censorship services to their peers. Each nation buying into China’s Community for a Shared Future may well be a case study on the successful use of internet connectivity without increasing political risks: a world with fewer Arab Springs or “color revolutions.”
No comments:
Post a Comment