Alexander Brown, Nis Grünberg
Key findings
 China regards hydrogen as a strategic “frontier technology” in which it aims to become a global leader. Its policy focus in the short term will be on general industry development first, greening second.
China regards hydrogen as a strategic “frontier technology” in which it aims to become a global leader. Its policy focus in the short term will be on general industry development first, greening second.
China is poised to rapidly expand its green hydrogen industry within the next decade. Government mandates to decarbonize, along with the lure of growing demand for carbon-neutral hydrogen and associated equipment is spurring on related R&D and business ventures.
Local policy and industry developments are already moving far beyond the national strategy and its conservative targets, building momentum for the green hydrogen industry.
China’s push into green hydrogen will be characterized by strong state-led support for market creation and technology at each stage of the value chain. State-owned enterprises and public-funded R&D centers are rushing to develop hydrogen technologies with the expectation of a massive ramping up of the industry.
Driven by bullish forecasts for future demand in low-carbon hydrogen, private enterprise is also contributing to the rapid capacity expansion in green hydrogen production equipment.
Europe’s leadership in green hydrogen technology will shrink as China deepens its innovation capacities and strengthens its price competitiveness. The country already accounts for a third of global electrolyzer manufacturing capacity and will become more competitive as it scales up production.
Despite a surge in resources dedicated to hydrogen R&D, China remains behind Europe, the United States, and Japan in advanced technological capabilities. Industry experts in China estimate it will take at least five years before domestic technology catches up to global industry leaders.
European companies engage with Chinese firms as suppliers as well as R&D and joint-venture partners. The benefits for the European side should be weighed against the risks associated with accelerating the development of Chinese manufacturers.
1. China’s hydrogen ambitions in the global green technology race
Hydrogen will play an important role in the global energy transition. It is estimated that hydrogen will account for 10–12 percent of China’s energy consumption by 2050, and as much as 22 percent globally.1 For the country to reach this point sustainably and in line with its emission targets, cheap and scalable green hydrogen technology such as electrolyzers is needed. As costs for carbon-intense fuels increase and electrolysis technology becomes more advanced and efficient,2 green hydrogen is expected to reach price parity with currently cheaper gray hydrogen within a few years. Foreseeable demand, along with the fact that today several technologies compete, means the industry will become not only a lucrative market but also a field of intense competition, in China and internationally.
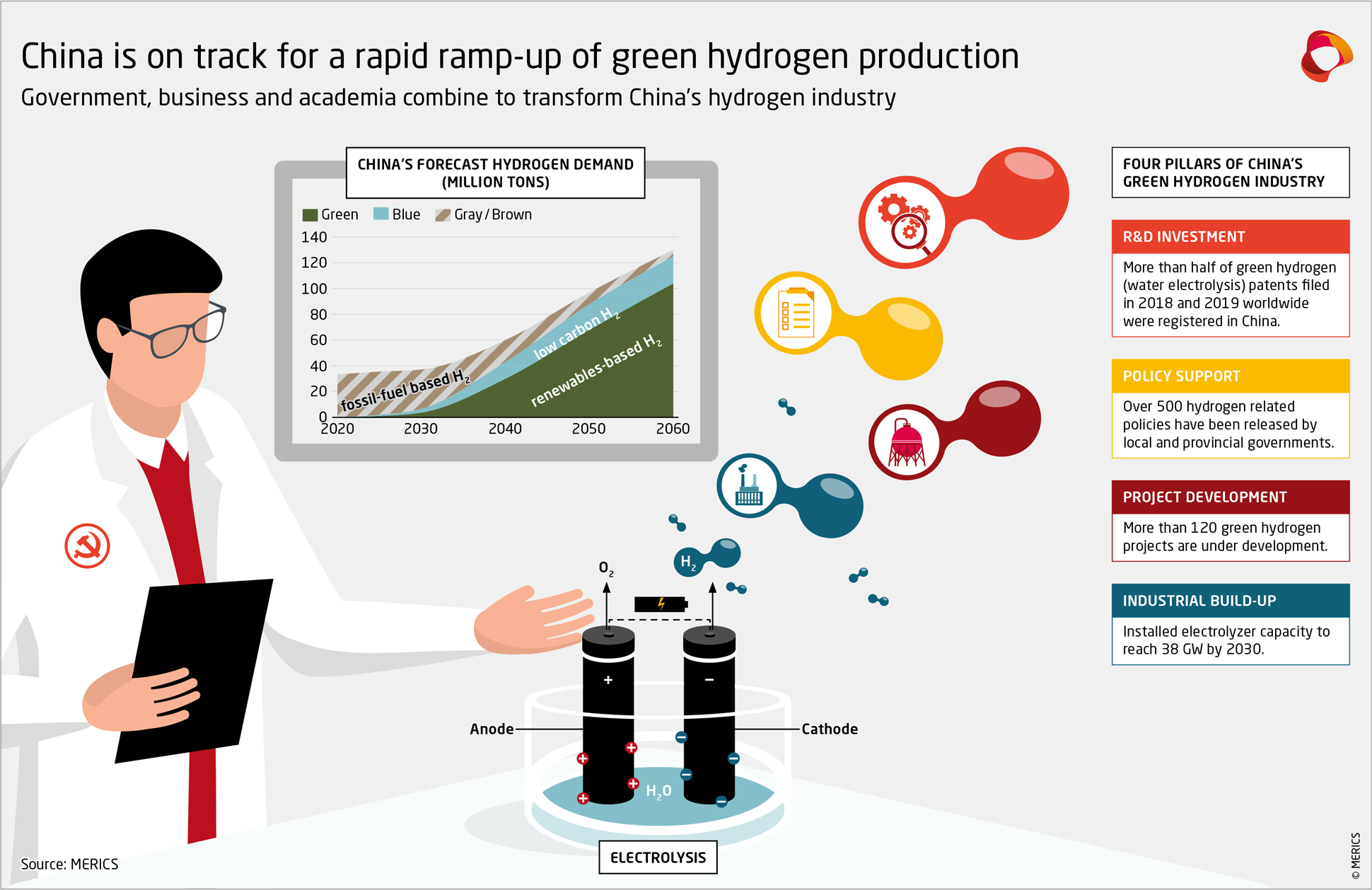
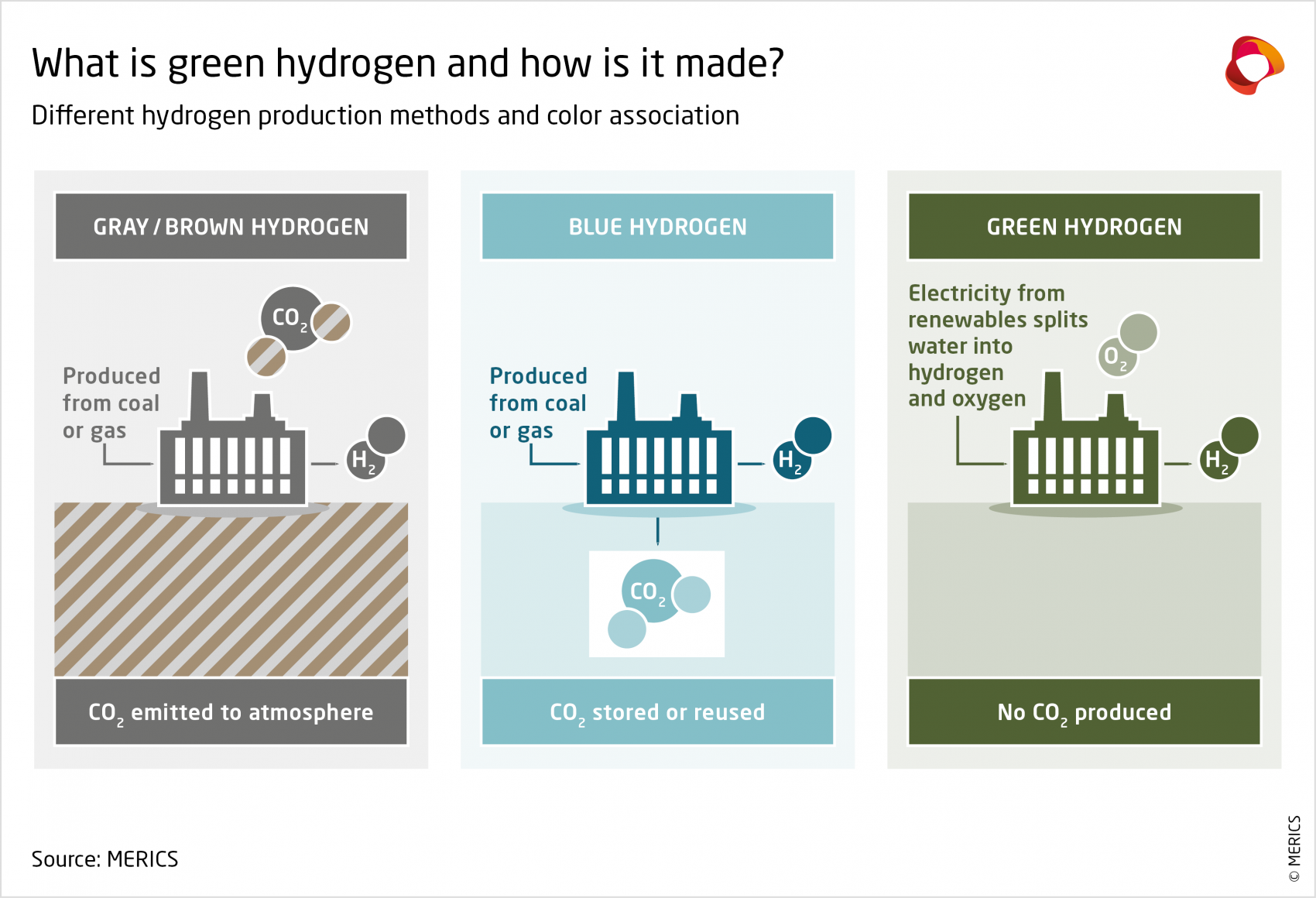
China is the world’s largest hydrogen producer with an annual output of 33 million tons, over a third of global demand.3 Hydrogen is used in, among other things, chemical, refining, and metal industries—either as an energy carrier (for example, providing heat or electricity in metallurgy) or as a feedstock (for example, for producing ammonia). While hydrogen is a “clean” energy carrier—reacting with oxygen, it produces only heat and water—producing it can have a significant CO2 footprint. China primarily produces brown and gray hydrogen by using coal or gas (respectively 60 percent and 20 percent of production)4 with high CO2 emissions. To meet its targets to achieve peak carbon emissions by 2030 and then reach carbon neutrality by 2060, green hydrogen—currently accounting for about 1 percent of production—will need to replace gray hydrogen as fast as possible (see Exhibit 1).
Exhibit 1
The Chinese industry’s outlook is strikingly positive. Current forecasts estimate China will reach 38 GW of electrolyzer capacity by 2030, and China’s premier hydrogen lobbying organization has called on the government to install as much as 100 GW by then.5 With only around 1 GW in operation and around 10 GW planned today, this illustrates how industry insiders and involved officials are betting on a massive ramping up of electrolysis capacity over the coming decade and beyond.
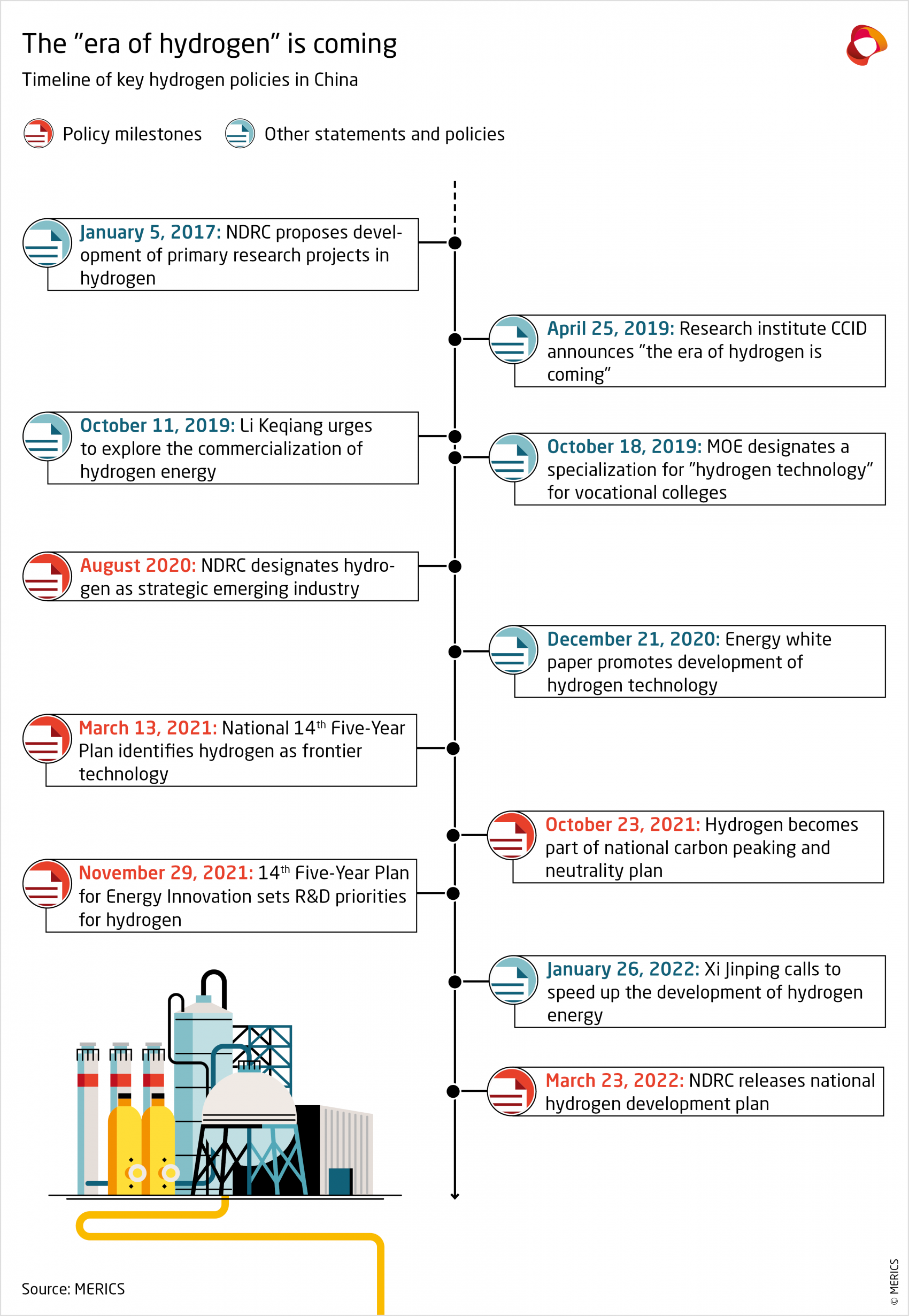
China’s plans for hydrogen come on the heels of those of other major economies that have adopted hydrogen development strategies in recent years. Although hydrogen was discussed as a strategic emerging technology for years, the European Union’s clean hydrogen strategy and Germany’s national strategy were issued only in 2020. China’s Medium and Long-term Plan for Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021-2035) was issued in March 2022. Compared to the EU and German strategies, which prioritize green hydrogen, China’s strategy is color-agnostic for now and only plans for green hydrogen to overtake gray and blue hydrogen after 2030.
Exhibit 2
At the subnational level, however, China’s local governments, research institutes, and industries are racing to develop hydrogen technology and markets. Provincial policy targets are more ambitious than the ones of the national strategy. A flurry in policy, research and development (R&D) activities, and industry developments show how the race for green hydrogen has started. As seen in the case of the solar photovoltaics (PV) and battery industries, China’s government-steered approach to creating markets, fostering technological innovation, and promoting industrial scaling can be very effective. Although still in its early stages, the country’s push into green hydrogen already shows that it will be characterized similarly by strong state-led support at each stage of the value chain, from research to technology, production, and applications—and that Chinese companies are eager to become major global players in the industry.
Exhibit 3
Exhibit 4
The province of Inner Mongolia alone aims to produce 500,000 tons of green hydrogen a year by 2025, more than double the target in the national strategy. Between 2020 and 2022, provinces announced they aimed to develop a hydrogen industry valued at CNY 756 billion in the coming five to ten years. More policies, project announcements, and large capacity targets are currently issued almost weekly.
These developments come off the back of years of heavy state investment into hydrogen R&D, which is increasingly focused on green hydrogen technology. Public research institutes, universities, state-owned enterprises (SOEs), and foreign firms all contribute, and they form partnerships to develop and demonstrate green hydrogen technologies. The number of related patents and academic articles is ballooning and the technological capabilities of domestic firms are growing.
China already makes up about a third of global electrolyzer manufacturing capacity. It can produce all key parts domestically with few exceptions (notably hydrogen valves) and local producers are very competitive on price.6 But they are not yet up to international standards in terms of efficiency and reliability, especially for large systems, according to industry insiders. As the number of demonstration projects grows, further investments are pouring into the upstream segments of the value chain. This will allow Chinese electrolyzer manufacturers to scale up, refine their technologies, and pose an increasing challenge to foreign firms for market share within and outside of China.
2. Industrial policy adds momentum to the creation of China’s hydrogen economy
Industrial policy – encompassing development plans, innovation targets, public finance, etc. – is a key driver of the development of China’s energy industry. State support has been instrumental to the success of past attempts to foster new green technology industries such as solar and wind. The country’s economic and industrial scale, government backing, and low production costs have enabled Chinese producers of, for example, PV and batteries to squeeze global competitors, on price and capacity if not always on best-in-class quality. The increasing policy support and growing volume of R&D investments prove that hydrogen is an industry in which China aims to kick-start a similar process.
Exhibit 5
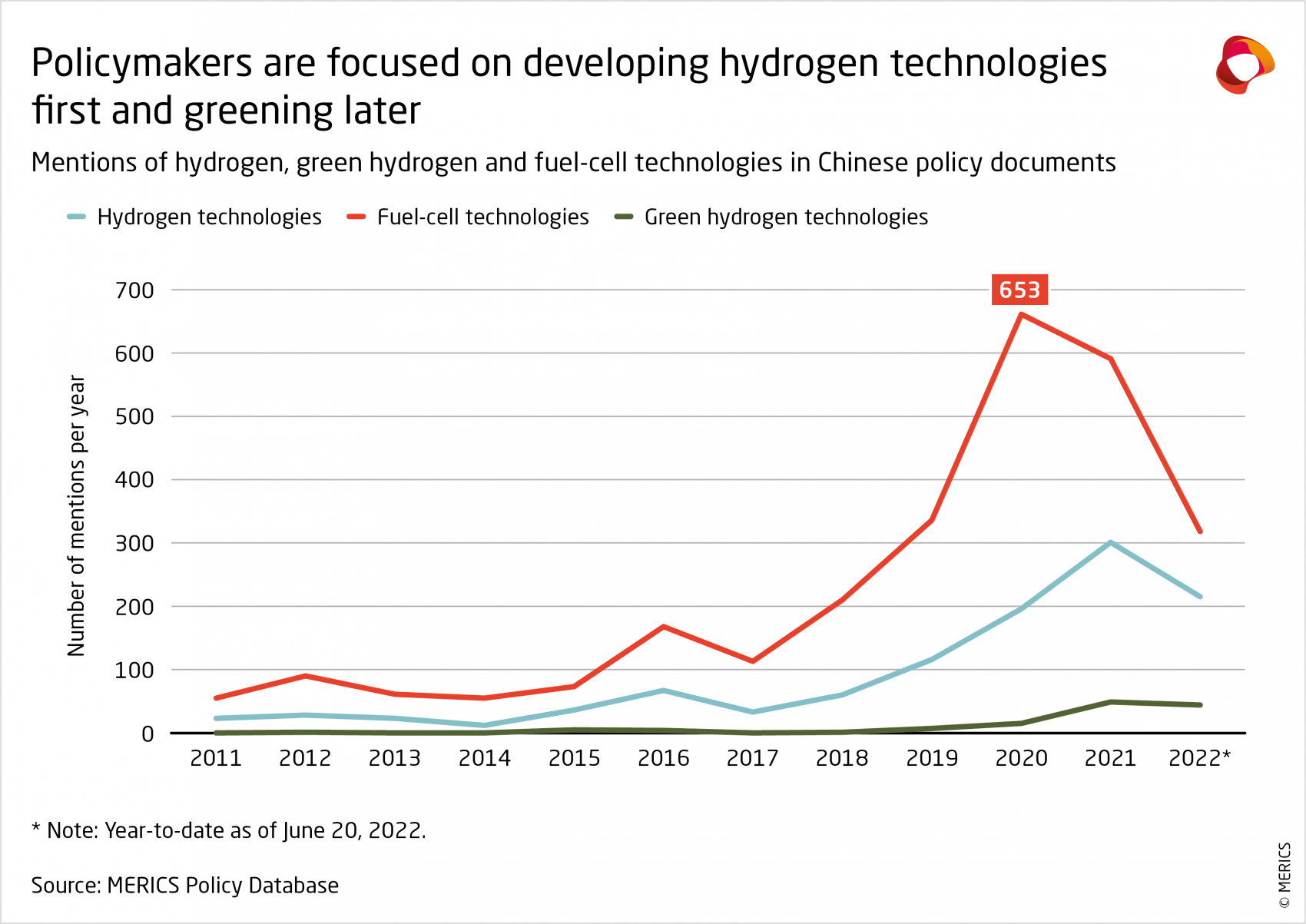
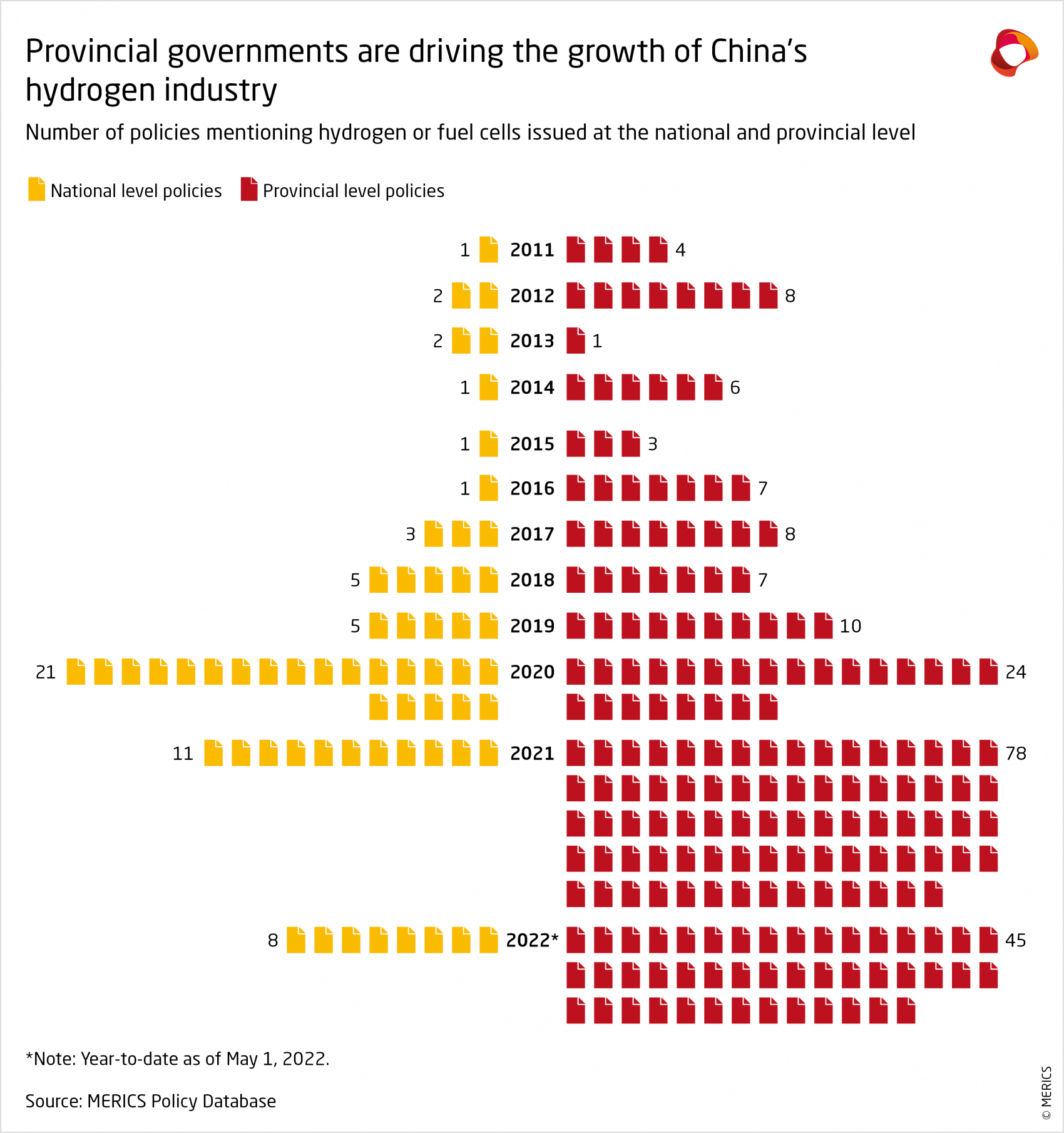
A steep increase in the number of policy statements by central and local governments shows how much attention has shifted in China towards developing the industry in recent years. After first being included in the 2006 national technology development plan, hydrogen was recognized in the Energy Law as an energy source for the first time in 2019. In 2020 hydrogen was further declared a strategic emerging industry by China’s main industry planner, the National Development and Reform Commission, which called to “accelerate the development of the new energy industry” including hydrogen.7 Fuel-cell technologies and vehicles (FCVs) have received the most attention, with China today among the leading nations in this field.
Fuel-cell vehicles feature prominently in China’s early hydrogen push
Much of China’s industrial policy in the hydrogen industry so far is focused on developing and demonstrating fuel-cell vehicles. They look likely to play a strong role in the decarbonization of the commercial vehicle market in particular, while batteries could be more suitable for powering passenger vehicles. Several local hydrogen plans have set targets for the number of FCVs to be rolled out in the short term. Beijing, Shanghai, and the provinces of Hebei, Inner Mongolia, and Shandong each aim to have 10,000 FCVs on their streets by 2025. Central-government funding also supports the growth of FCVs, including via a program offering financial rewards to city clusters for the industrialization of core fuel-cell technologies. Up to CNY 1.7 billion will be awarded to local governments that meet specific targets. But the contribution of FCVs to China’s energy transition depends on the supply of low-carbon hydrogen. Today, most of the hydrogen used to power them is produced using fossil fuels.
2.1 National policy remains vague on green hydrogen for now
For now, national policy support for hydrogen remains mainly focused on general industry development first and greening it second. This is part of China’s broader push for industrial upgrading, technological innovation, and long-term transition towards clean energy. Compared to European strategies, which aim to leverage green hydrogen for rapid and deep decarbonization, China’s national policies are marked by the absence of open, market-based mechanisms to drive development. Instead, the emerging pattern resembles the country’s preferred state-capitalist approach of relying on local governments, R&D centers, and SOEs to establish an industry around strategic policy targets.
Exhibit 6
China’s national hydrogen strategy is conservative on quantitative targets. Its aim of 100,000 to 200,000 tons of annual green hydrogen production by 2025 is dwarfed by the EU’s annual target of one million tons. Germany’s plan for a 14 terawatt-hours (TWh) production capacity in 2025 is more than twice that of China’s stated maximum goal of 6.7 TWh (see Exhibit 7). Such conservative targets are puzzling, given that industry insiders estimate that its existing green hydrogen production capacity has already reached 100,000 tons a year.8 However, a more specific policy for decarbonizing the existing hydrogen industry is planned as part of China’s national decarbonization strategy (known as the 1+N framework to reach the 2030 and 2060 targets). This will likely introduce more concrete targets for hydrogen applications and integration in the energy system. Lastly, more targeted financial mechanisms, such as subsidies, have been used in other sectors in the past, and could be used to further drive the development of the industry.
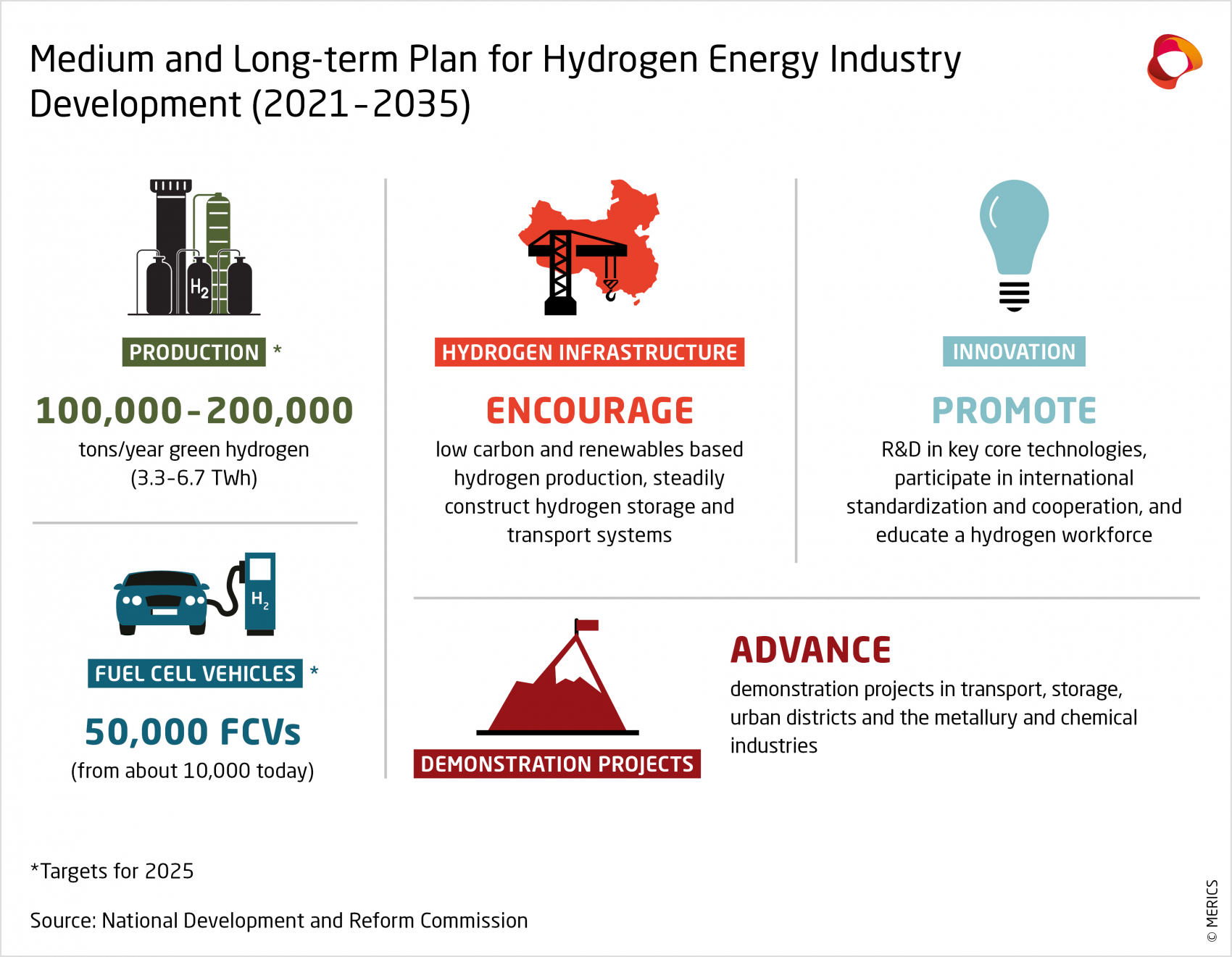
Exhibit 7
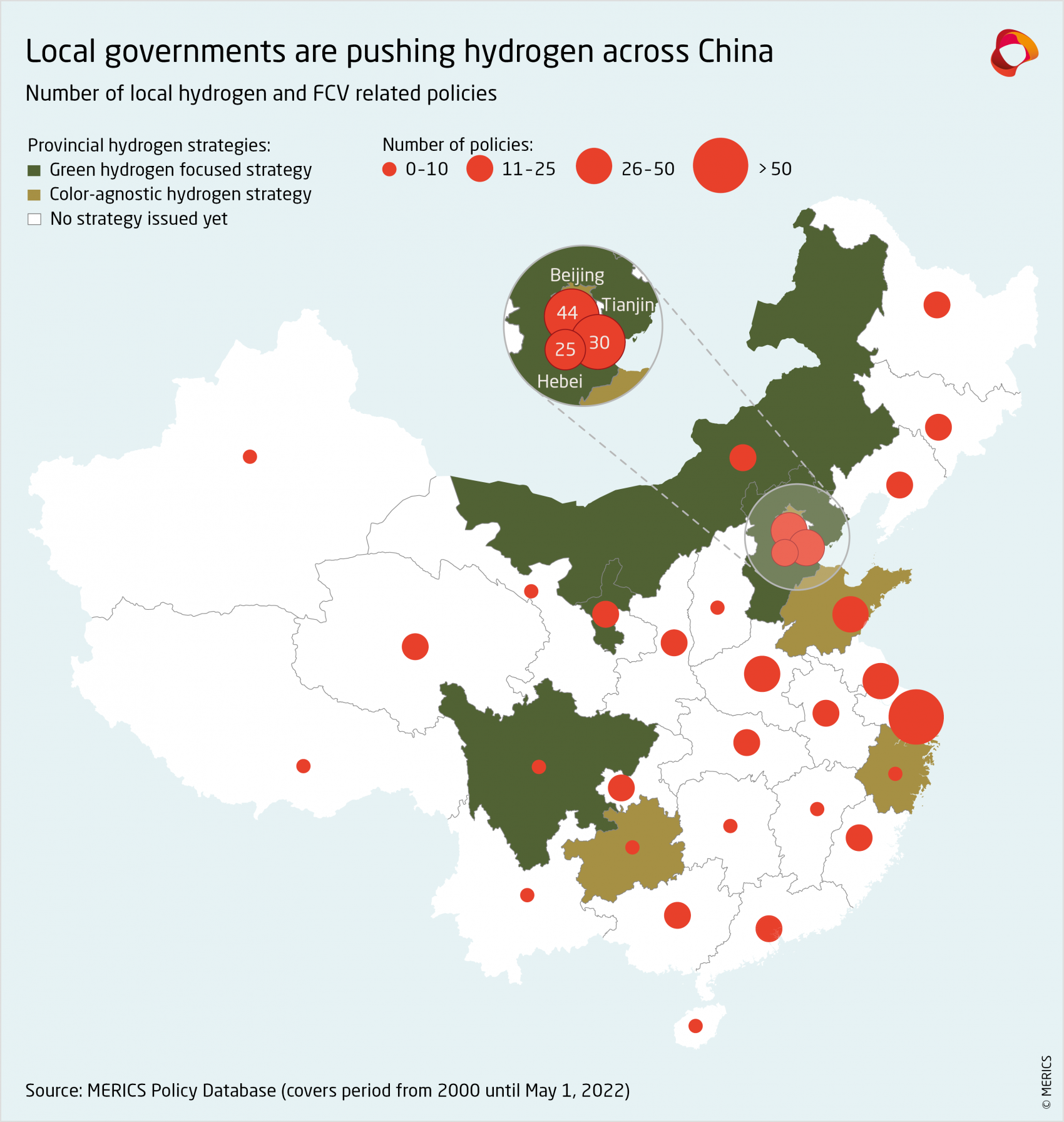
2.2 Provinces are driving development beyond Beijing’s targets
While China’s national targets are conservative, local governments have been extremely active in driving the development of hydrogen industries, including increasingly green hydrogen. About 30 local governments mentioned hydrogen in their 14th Five-Year Plans and over 50 cities have issued policies to grow their local hydrogen industry. Nine provinces have so far issued major development plans for hydrogen and related industries.
Exhibit 8
Provincial development plans vary in their industry focus and the degree to which they prioritize green hydrogen. Ten provinces have already adopted specific hydrogen strategies (not counting hydrogen fuel cell and FCV plans). Hebei, Inner Mongolia, and Sichuan focus on green hydrogen specifically. There is an emerging pattern of provinces rich in renewable energy integrating their solar, wind, and hydro resources into their hydrogen strategies. These provinces feature the development of green hydrogen and related industries more prominently. By comparison, the coastal provinces with their advanced industries tend to remain more color-agnostic. These often focus on hydrogen-related applications such as FCV, downstream applications, and technological innovation.
The trend, however, is clear: entrepreneurial officials in local governments and SOEs are beginning to view green hydrogen as an attractive means to achieve decarbonization targets and are also eying the bullish market expectations for green hydrogen technology. Stricter regulation and rising prices for carbon-intense operations further provide incentives for local officials to look for new and sustainable solutions such as green hydrogen, hoping to spur or protect economic development within their jurisdiction.
Becoming a green hydrogen leader: Inner Mongolia
Rapid capacity expansion around major, often SOE-backed, projects illustrates how provinces rich in renewable energy partner with energy companies to leverage their resources. They follow national policy impulses but set their own ambitious targets in an attempt to develop new growth opportunities and to respond to expectation of growing demand for clean energy and green technologies.
Inner Mongolia has vast solar and wind resources, making it an ideal place for green hydrogen production. In 2021, it announced seven large green hydrogen projects in the province, totaling 2.2 GW capacity powered by wind and solar, producing 67,000 tons green hydrogen annually upon completion around 2023. The province’s production target for 2025 is 500,000 tons, far greater than the national target of 100,000–200,000 tons.
China’s corporate sector has responded to the favorable policy environment in the province. The energy SOE Jingneng has announced plans to build a 5 GW solar-wind power base to produce additional green hydrogen in excess of 400,000 tons annually.
3. The innovation launchpad for China’s hydrogen takeoff
China’s leadership is committed to developing strong technological capabilities in all areas of the hydrogen value chain to profit from the economic and environmental benefits that it promises to deliver. The race is on to innovate and create the emerging technologies that will sustain the green hydrogen industry of the future. The government calls on public and private institutions to work towards technological innovation in strategic areas. State funds support public universities and research institutes to conduct research while SOEs and private enterprises pursue R&D in high-priority areas. China’s innovation push into hydrogen has led to a steep rise in related patents and academic articles in recent years. But it still has a way to go before it can match the cutting-edge technology being developed in other advanced economies, particularly in Europe.
3.1 Beijing ramps up national R&D funding
China’s expenditure on hydrogen-related R&D has surged since 2015. According to the International Energy Agency and Mission Innovation, its investment in this field increased sixfold between 2018 and 2019. In the process, China’s spending surpassed that of the United States and Europe combined.9
The development of green hydrogen technology benefits from the clustering of R&D funding, local policy support, and collaboration with industries. The National Key R&D Programs (NKPs) are China’s highest-level R&D funds for applied technology and the second-largest channel for public R&D funding.10 NKP projects are usually awarded to a consortium under a research institution (university, state research institute, or company).
Since 2016, the government has announced 66 NKP projects focusing on hydrogen technologies, with a total estimated value between CNY 1.75 and CNY 5 billion.11 Of these, 14 NKPs have an explicit focus on green hydrogen, with a combined estimated value between CNY 400 million and CNY 1.25 billion.12 Green hydrogen has only just recently received substantial support through this channel. Eleven of the green hydrogen NKPs were announced in 2021, while the other three were launched in 2018. These projects promote research into established (alkaline) and emerging (proton-exchange membrane—PEM) electrolyzer technologies, and they aim for advances in the cost, efficiency, power, and scalability of renewable hydrogen production.
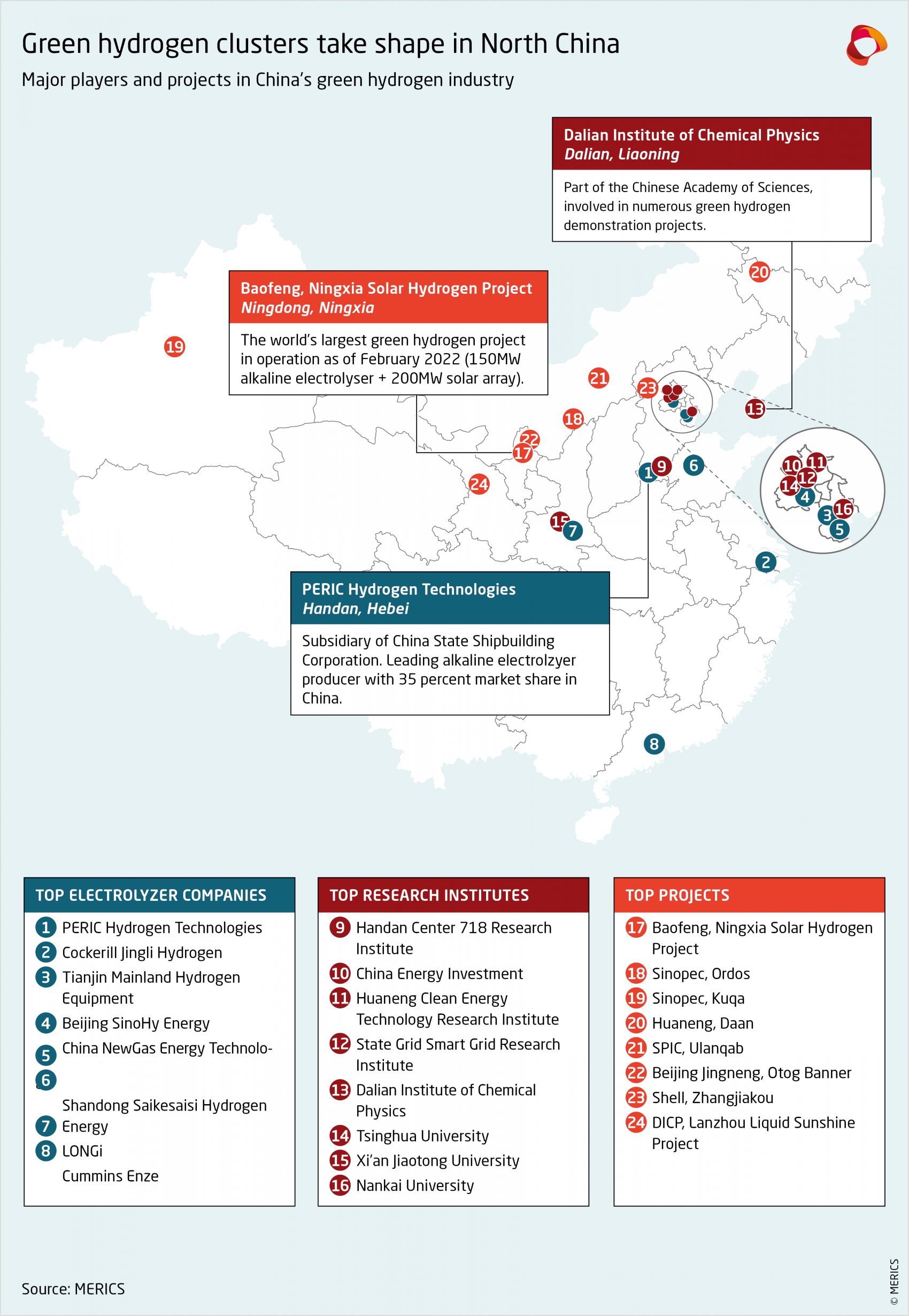
The recipients of NKP funding for research into hydrogen technologies are concentrated in the northern and coastal regions. Several of the research institutes involved house relevant State Key Laboratories, which also contribute to the development of hydrogen technologies.13 For instance, in 2019 the laboratory on catalysis at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), developed and trialed a new generation of catalyst for highly efficient alkaline electrolysis.14
Almost all the leading innovators in China’s green hydrogen sector are directly funded or controlled by the government, be they public universities, the CAS,15 or SOEs. China’s policymakers facilitate the growth of the domestic innovation ecosystem through actively encouraging cooperation among universities, enterprises, and international actors. The CAS acts as a central node of cross-institute partnerships in academic papers on green hydrogen, and it collaborates with enterprises on patents.16 It has worked with the likes of PetroChina, Boeing, and Shell to develop multiple patent families.17
SOEs are the main force behind the demonstration projects promoting new hydrogen technologies. For example, in December 2021 a megawatt-scale PEM pure-water electrolysis hydrogen production system and fuel-cell system were set up in Luan, Anhui province, by a subsidiary of State Grid Corporation of China working together with the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics. This was allegedly the first project involving such equipment in China with independent intellectual property rights.18 A month earlier, Huaneng Energy announced it had developed the world’s largest single-cell alkaline electrolyzer, with a capacity of 1,300–1,500 normal cubic meters of hydrogen per hour. The project involved its Clean Energy Technology Research Institute (HCERI) and the Belgian-owned Cockerill Jingli Hydrogen.19
3.2 China emerges as a potential challenger in hydrogen research
R&D support for hydrogen has led to a sharp increase in patent applications in China, to the point where the number of Chinese patents exceeds that of the rest of the world combined. But policy mechanisms have also led to an increase in the number of junk patents, meaning that China’s technological capabilities are not as advanced as they seem.
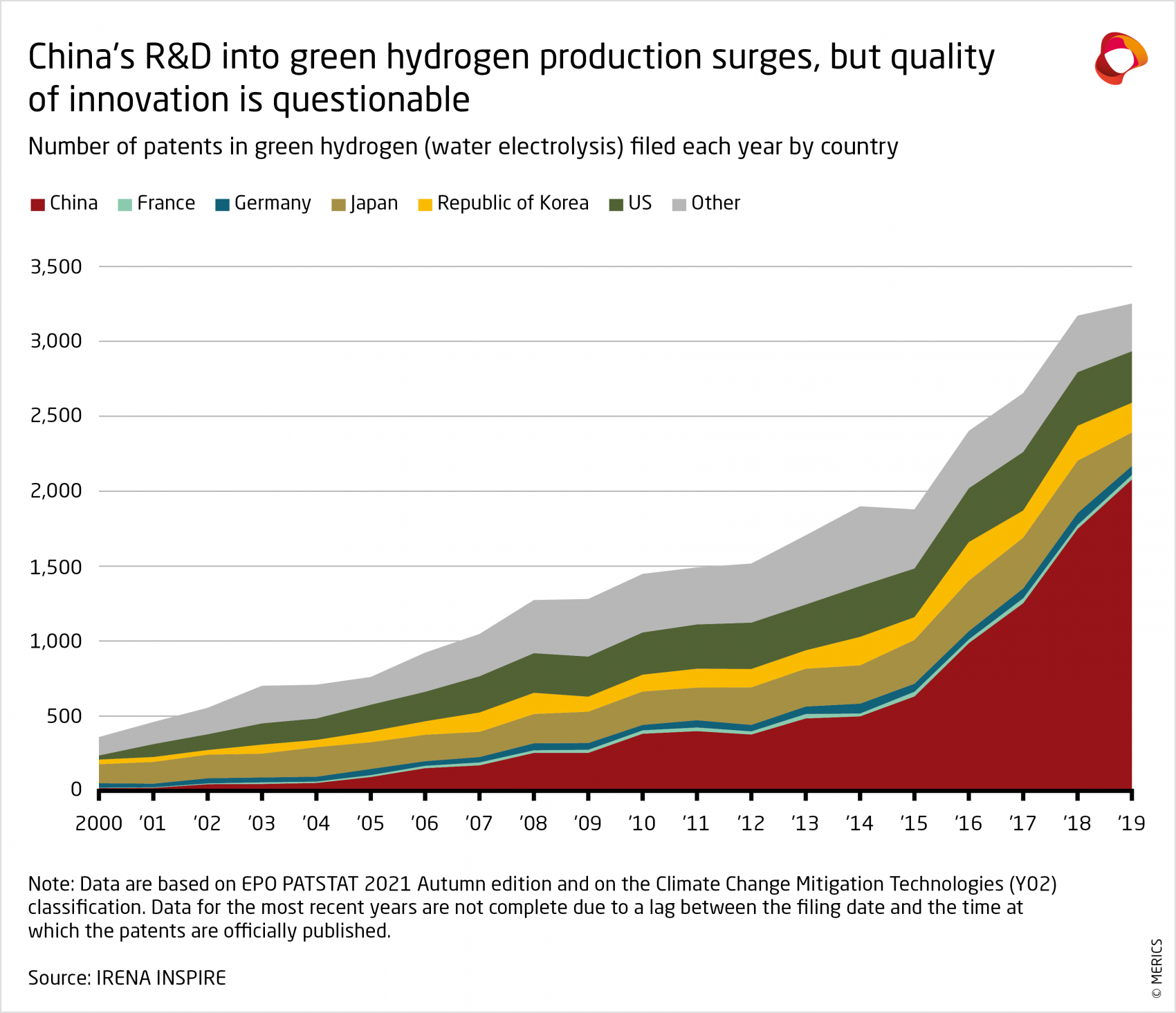
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the number of patents related to green hydrogen production filed in China has shot up since 2015. As a result, China’s global share of patents in the field of green hydrogen (water electrolysis) had risen to almost two-thirds by 2019 (see Exhibit 9).20 Developments in academia have followed the same trend, with the number of research papers on green hydrogen published in China steadily increasing between 2010 and 2019.21 China accounted for almost 40 percent of academic papers on green hydrogen published between 2010 and 2020.
Exhibit 9
However, the growth in hydrogen-related patents reflects a broader trend in Chinese patents. The number of patent applications and patents granted in China has skyrocketed over the past two decades, to the point where they now far outnumber those registered in the EU and the United States.22 Government incentives provide direct financial subsidies to patent filers in addition to tax breaks and other social benefits. This has caused companies and individuals to register patents to take advantage of subsidies and other rewards rather than to protect valuable innovation.23
Between 2015 and 2019, only about six percent of Chinese patents were filed abroad, compared to almost half of European patents and about a third of US patents.24 This likely reflects the lack of quality patents and a reduced need to protect them abroad as well as domestically. The below-average citation rate of Chinese patent filings abroad also indicates that they are of lower quality compared to foreign patents.25
International patent families (IPFs)—a collection of patent applications relating to a specific invention taken out in different countries—are a strong indicator of high-quality innovation activity. OECD data on patents filed in at least two locations shows that China has registered far fewer hydrogen-related international patents (not including fuel-cell related patents) compared to other established leaders. In 2019, China registered just 40 such patents, far less than the EU (193), the United States (138) and Japan (110).26
Europe has led the development of hydrogen production and storage technologies, including electrolyzers, over the past decade. It accounted for 40.2 and 31.3 percent of global IPFs in the fields of hydrogen storage and production respectively between 2010 and 2019, compared to China’s shares of 1.5 and 4.6 percent.27
Behind the appearance produced by its artificially boosted patent numbers, China is playing catch-up and will still require several years if it is to make real breakthroughs and develop competitive solutions that are entirely domestically produced. In a 2021 survey, the majority of Chinese industry experts estimated that it would take five years or more for the country to catch up with internationally advanced technologies in hydrogen and fuel cells.28
4. Corporates begin building China’s green hydrogen future
The corporate sector is driving China’s technological catch-up in green hydrogen. With decarbonization locked in for the medium to long term, the green hydrogen industry is poised to undergo massive expansion, and energy SOEs will play a key role in the planning and financing of related projects. Interest is surging, fueled by China’s rapid rollout of renewable energy, its growing electrolyzer manufacturing capacity as well as the reduced costs of electrolysis installations. Bloomberg expects China will make up over 60 percent of global electrolyzer installations in 2022.29
4.1 Testing the water: SOEs launch first major green hydrogen projects
There are currently over 120 green hydrogen production projects at different stages of development in China, with several gigawatt-scale projects announced over the past two years.30 These are primarily located in inland regions—such as Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, and Xinjiang—where renewable energy potential is abundant.
Most green hydrogen projects to date have been financed by large energy SOEs.31 China’s SOEs dominate the energy and heavy industry sectors and are pushing into all segments of the hydrogen value chain.32 According to China’s SOE watchdog, the State-Owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, as of 2021 one-third of SOEs had plans to expand their operations in the hydrogen industry, whether in production, storage, refueling, or related businesses.33
For instance, Sinopec, which is already a dominant player in the hydrogen sector, has announced it aims to become China’s leading hydrogen company by 2025 and will reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2050 (ten years ahead of the national target). It expects to produce 500,000 tons of hydrogen a year from renewable energy sources by 2025 and plans to expand its network of hydrogen transport pipelines.35 Sinopec is building green hydrogen production facilities in Ordos, Inner Mongolia, and Kuqa, Xinjiang, with planned annual outputs of 10,000 and 20,000 tons respectively. These projects are scheduled to be operational by June 2023.36
Private companies in the renewable-energy industry are also increasingly integrating green hydrogen into their business plans. The solar project developer GCL New Energy has announced it aims to build 100 energy stations by 2025 with an annual production capacity of 400,000 tons of green hydrogen. It has also partnered with two financial companies to create a CNY 10 billion hydrogen investment fund.37
4.2 China’s electrolyzer manufacturing industry is set for more competition
Electrolyzers are the primary technology that makes the production of zero-emissions hydrogen via renewable energy possible. They underpin the entire low-carbon transition that green hydrogen promises to enable across mobility, industry, and other sectors. As of 2021, China accounted for 35 percent of global electrolyzer manufacturing capacity, and Europe 60 percent.38 Estimates for 2022 suggest Europe has already reached 2.5 GW while China could expand capacity to 1.5-2.5 GW.39
Three companies dominate the Chinese market for alkaline electrolyzers: PERIC Hydrogen Technologies (affiliated with 718 Research Institute of China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation), Cockerill Jingli Hydrogen,40 and Tianjin Mainland Hydrogen Equipment.41 These companies straddle the public and private sector and have significant R&D capacities. They are well placed to grow into national champions and reap the benefits of surging demand for green hydrogen equipment. But competition will increase as the market grows, and advances in other green hydrogen technology, notably PEM, could also shift demand in other directions.
Although PEM technology today is significantly more expensive and makes up a smaller share of the Chinese market, potential performance benefits and a lack of established suppliers in this field mean that most new entrants to the electrolyzer market are pursuing PEM.42 China’s largest state-owned power company, State Power Investment Corporation (SPIC)43 has announced it will invest CNY 10 billion in a project based in Changchun to develop high-end PEM equipment, including a manufacturing base with an annual output of 40 GW.44 The leading solar PV inverter supplier, Sungrow Power Supply, set up a dedicated hydrogen subsidiary in June 2021.
In recent years, China-based producers of green hydrogen technology have progressively increased the share of components sourced locally. China is actively seeking to replace imported parts with domestic alternatives to increase supply-chain security across all sectors. Gaps exist in areas as such hydrogen valves and local producers still lag behind manufacturers in Europe and the United States when it comes to PEM electrolyzers.45
But on the whole, domestic hydrogen technology has become more competitive, especially in fuel cells, membranes, and alkaline electrolysis. Despite past concerns about their quality in terms of reliability and durability, the manufacturing capabilities of Chinese producers are improving. This increases China’s ability to leverage industrial clusters and economies of scale to drive costs down.46 What Chinese technology cannot provide in efficiency, it can make up for in price. Chinese-made electrolyzers are already significantly cheaper than foreign equipment and further scaling up production in the years ahead will work in China’s favor.47
4.3 Companies flock for a piece of the equipment-supplier pie
Domestic manufacturers are pouring investment into expanding electrolyzer production facilities, leading to a growing number of demonstration projects for electrolysis technology. All major existing producers are scaling up capacity and new players are looking to enter the market. The solar panel manufacturer LONGi intends to expand its electrolyzer production capacity from 500 MW to 2 GW by the end of 2022, and further to 5–10 GW in the coming years.48 SPIC plans to build 10 GW of electrolyzer manufacturing capacity by 2027.49 This is in line with other gigawatt-scale electrolyzer factories announced by leading manufacturers such as Thyssenkrupp, Siemens, McPhy, or Cummins.
China-based electrolyzer manufacturers are not only focused on domestic demand, but also eying the overseas market. PERIC Hydrogen Technologies, Cockerill Jingli Hydrogen, and Shandong Saikesaisi have already begun exporting equipment. It is possible that a delayed transition from gray to green hydrogen, for example, due to resistance from existing producers of fossil-based hydrogen, will further push Chinese manufacturers to find customers overseas. Other constraints on the expansion of the domestic market could be the slow rollout of transport infrastructure or the lack of capacity to turn hydrogen into easier to handle molecules such as ammonia, such that consumption remains restricted to locations close to production sites.
Foreign firms are deeply involved in China’s emerging green hydrogen industry as suppliers, R&D partners and joint-venture partners. Among the most important has been Belgium’s Cockerill Jingli Hydrogen, which helped Huaneng produce the world’s first 1,300 normal cubic meters per hour alkaline electrolyzer.52 The Belgian company has previously worked with the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics to develop electrolysis technology.53 In 2021, Cockerill Jingli Hydrogen supplied electrolyzers for the Beijing Olympic Games as well as for Baofeng’s Ningxia PV-hydrogen power plant.54 Similarly, Siemens Energy supplied electrolyzers to a megawatt-scale production facility connected to a hydrogen fueling station near Beijing in the lead up to the 2022 Winter Olympics.55
Key Chinese players have established joint ventures with foreign firms to develop advanced technologies and even target export markets. Sinopec reached an agreement with the US firm Cummins to set up a 50/50 joint venture to promote Cummins’ PEM electrolysis technology in China. The partners will build a factory in Foshan, Guangdong, with 500 MW of annual capacity by 2023, ramping up to 1 GW over five years.56 Norway’s designer and supplier of hydrogen plants—HydrogenPro—is teaming up with Tianjin HQY Hydrogen Machinery. This joint venture intends to set up an electrolyzer production facility in Tianjin with an annual capacity of 300 MW and to export electrolyzers globally.57
The lure of increased sales and China’s strengths in manufacturing has already enticed several European electrolyzer firms to join forces with local players and produce in the country. This will help China progress toward its long-term goal to become a leader in green hydrogen technology. However, foreign firms and governments ought to take precautionary measures to ensure that they do not sacrifice their long-term competitiveness for short-term gain.
5. China’s green hydrogen industry starts small but on track for fast growth
China has set its sights on the hydrogen era and wants to be part of the global development of the industry. At this stage, national policy is concentrated on industry and technology development rather than green hydrogen specifically, but that is set to change in the medium term. At the subnational level, the market outlook for green technology, R&D activities, and demand for climate-friendly energy solutions are driving green hydrogen beyond the conservative national policy targets.
So far, the central government has refrained from using subsidies or other significant financial support to push green hydrogen, leaving it with a potent tool in reserve to further drive the industry once priorities shift from developing the hydrogen industry at large to green hydrogen. The preoccupation with energy security and stable power supply means that a clear policy preference for green hydrogen is currently unlikely.
Yet three factors could quickly accelerate demand in China and globally for electrolyzers and green hydrogen technology in the near future:
First, the country takes its climate targets seriously and green hydrogen is set to be a central part of the long-term solution for a secure and sustainable energy system. China must switch to green hydrogen as fast as possible if it wants to decarbonize its gray and brown-hydrogen-guzzling industries.
Second, the rising cost of fossil fuels and the various carbon pricing systems under development in major economies are pushing green hydrogen towards price parity with the still cheaper gray hydrogen.
Third, growing energy-security concerns provide additional momentum. The shift away from imported fossil fuel, including “transitional” gas, is accelerating globally as an effect of the Ukraine war. Green hydrogen looks increasingly attractive and needed given the advanced timeline of decarbonization now discussed in the EU, China, and elsewhere.
China’s capabilities will evolve in an industry that sees tremendous growth potential, global competition for green technology, and local governments looking for new sources of growth that align with Beijing’s decarbonization and innovation objectives. There is a groundswell of local policy support for green hydrogen, alongside R&D and demonstration projects led by SOEs and public research centers. The evolving ecology is already leading to a developmental surge in domestic technology. While not yet competitive with technology leaders such as Siemens, Thyssenkrupp and Cummins, Chinese companies are catching up.
For the time being, the danger of China surpassing Europe’s technological edge appears limited. Europe remains at the forefront of hydrogen technology and the ambitious targets set within the EU and national strategies for hydrogen have established a sound environment for continued innovation and industrial growth. But as China scales up its production of green hydrogen technologies, it will become a serious challenger to Europe’s technology leaders and attempt to replace foreign suppliers with domestic technology in its growing market for electrolyzers.
Given China’s vast consumption of hydrogen, overcapacity is currently no issue. Because of the current gap between its overall demand for hydrogen and low-carbon production, it is unlikely China will become a major exporter of green hydrogen, nor is this planned in national policy. Demand will increase further as broader industrial and residential applications, as well as transport solutions to get hydrogen from the large production centers to places of consumption, are developed.
Mass adoption of green hydrogen for commercial applications in China is expected to begin within the next decade.58 By the time green hydrogen begins to establish itself as an important part of China’s energy supply from 2030 onwards, China will have champions in related technologies all along the value chain, leading to increased competition within China and in third markets.
European firms can benefit from participating in China’s burgeoning new industry. The country will be a key market for their technology, and it presents opportunities for collaboration on research and standard setting. But they also need to manage the associated risks and take measures to avoid overreliance on Chinese sales, protect their intellectual property and maintain their technological edge.
China’s ambitions in hydrogen can be viewed as both a blessing and a curse. Chinese technology developers and producers will likely make a valuable contribution to global efforts to combat climate change by driving down the cost of related technologies, but they will also increase competition for foreign players. European policymakers and business leaders ought to pay close attention to the evolving policy-aided ecosystem around green hydrogen in China and consider its impact on European industries as well as the energy transition in Europe and abroad.