Tom Uren , Elise Thomas
Tweeting through the Great Firewall
Preliminary Analysis of PRC-linked Information Operations on the Hong Kong Protests
Introduction
On August 19th 2019, Twitter released data on a network of accounts which it has identified as being involved in an information operation directed against the protests in Hong Kong. After a tip-off from Twitter, Facebook also dismantled a smaller information network operating on its platform. This network has been identified as being linked to the Chinese government.
Researchers from the International Cyber Policy Centre (ICPC) at the Australian Strategic Policy Institute have conducted a preliminary analysis of the dataset. Our research indicates that the information operation targeted at the protests appears to have been a relatively small and hastily assembled operation rather than a sophisticated information campaign planned well in advance.
However, our research has also found that the accounts included in the information operation identified by Twitter were active in earlier information operations targeting political opponents of the Chinese government, including an exiled billionaire, a human rights lawyer, a bookseller and protestors in mainland China. The earliest of these operations date back to April 2017.
This is significant because—if the attribution to state-backed actors made by Twitter is correct—it indicates that actors linked to the Chinese government may have been running covert information operations on Western social media platforms for at least two years.
Methodology
This analysis used a mixed-methods approach combining quantitative analysis of bulk Twitter data with qualitative analysis of tweet content.
The dataset for quantitative analysis was the tweets and accounts identified by Twitter as being associated with a state-backed information operation targeting Hong Kong and is available here.
This dataset consisted of
account information about the 940 accounts Twitter suspended from their service
The oldest account was created in December 2007, although half of accounts were created after August 2017
3.6 million tweets from these accounts, ranging from December 2007 to May 2019
The R statistics package was used for quantitative analysis, which informed phases of social network analysis (using Gephi) and qualitative content analysis.
Research limitations: ICPC does not have access to the relevant data to independently verify that these accounts are linked to the Chinese government; this research proceeds on the assumption that Twitter’s attribution is correct. It is also important to note that Twitter has not released the methodology by which this dataset was selected, and the dataset may not represent a complete picture of Chinese state-linked information operations on Twitter.
Information operation against Hong Kong protests
Indications of a hastily constructed campaign
Carefully crafted, long-running influence operations on social media will have tight network clusters that delineate target audiences. We explored the retweet patterns across the Twitter take-down data from June 2019 – as the network was mobilising to target the Hong Kong protests – and did not find a network that suggested sophisticated coordination. Topics of interest to the PRC emerge in the dataset from mid-2017 but there is little attempt to target online communities with any degree of psychological sophistication.
There have been suggestions that Taiwanese social media, during recent gubernatorial elections, had been manipulated by suspicious public relations contractors operating as proxies for the Chinese government. It is notable that the network targeting the Hong Kong protests was not cultivated to influence targeted communities; it too acted like a marketing spam network. These accounts did not attempt to behave in ways that would have integrated them into – and positioned them to influence – online communities. This lack of coordination was reflected in the messaging. Audiences were not steered into self-contained disinformation ecosystems external to Twitter, nor were hashtags used to build audience, then drive the amplification of specific political positions. As this network was mobilising against the Hong Kong protests, several nodes in the time-sliced retweet data (see Figure 1) were accounts to promote the sex industry, accounts that would have gained attention because of the nature of their content. These central nodes were not accounts that had invested in cultivating engagement with target audiences (beyond their previous marketing function). These accounts spammed retweets at others outside the network in attempts to get engagement rather than working together to drive amplification of a consistent message.

Figure 1: Retweet network from June 2019, derived from Twitter’s take-down data, showing the significant presence of likely pornography-related accounts within the coordinated network that targeted the Hong Kong protests.
This was a blunt–force influence operation, using spam accounts to disseminate messaging, leveraging an influence-for-hire network. The predominant use of Chinese language suggests that the target audiences were Hong Kongers and the overseas diaspora.
This operation is in stark contrast to the efforts of Russia’s Internet Research Agency (IRA) to target US political discourse, particularly through 2015-2017.
The Russian effort displayed well-planned coordination. Analysis of IRA account data has shown that networks of influence activity cluster around identity or issue-based online communities. IRA accounts disseminated messaging that inflamed both sides of the debates around controversial issues in order to further the divide between protagonist communities. High-value and long-running personas cultivated influence within US political discourse. These accounts were retweeted by political figures, and quoted by media outlets.
The IRA sent four staff to the US to undertake ‘market research’ as the IRA geared up its election meddling campaign. The IRA campaign displayed clear understanding of audience segmentation, colloquial language, and the ways in which online communities framed their identities and political stances.
In contrast, this PRC-linked operation is clumsily re-purposed and reactive. Freedom of expression on China’s domestic internet is framed by a combination of top-down technocratic control managed by the Cyberspace Administration of China and devolved, crowdsourced content regulation by government entities, industry and Chinese netizens. Researchers have suggested that Chinese government efforts to shape sentiment on the domestic internet go beyond these approaches. One study estimated that the Chinese government pays for as many as 448 million inauthentic social media posts and comments a year. The aim is to distract the population from social mobilisation and collective forms of protest action. This approach to manipulating China’s domestic internet appears to be much less effective on Western social media platforms that are not bounded by state control.
Yet, the CCP continues to use blunt efforts to grow the reach, impact and influence of its narratives abroad. Elements of the party propaganda apparatus – including the foreign media wing of the United Front Work Department – have issued (as recently as 16 August) tenders for contracts to grow their international influence on Twitter, with specific targets for numbers of followers in particular countries.
In the longer term, China’s investments in AI may lift its capacity to target and manipulate international social media audiences. However, this operation lacks the sophistication of those deployed by other significant state proponents of cyber-enabled influence operations; particularly Iran and Russia, who have demonstrated the capacity to operate with some degree of subtlety across linguistic and cultural boundaries.
This was the quintessential authoritarian approach to influence – one-way floods of messaging, primarily at Hong Kongers.
Use of repurposed spam accounts
Many of the accounts included in the Twitter dataset are repurposed spam or marketing accounts. Such accounts are readily and cheaply available for purchase from resellers, often for a few dollars or less. Accounts in the dataset have tweeted in a variety of languages including Indonesian, Arabic, English, Korean, Japanese and Russian, and on topics ranging from British football to Indonesian tech support, Korean boy bands and pornography.

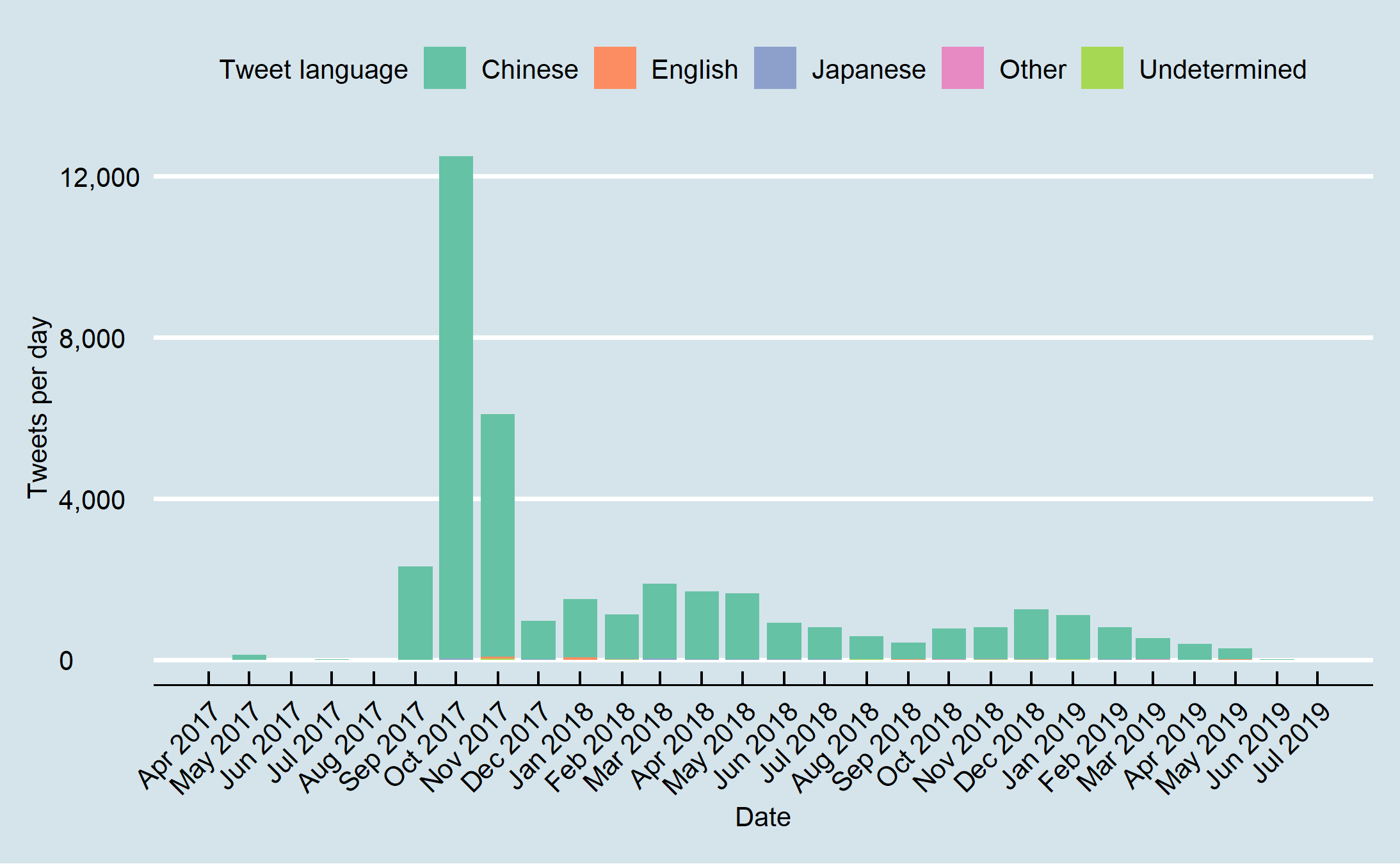
This graph shows the language used in tweets over time, (although Twitter did not automatically detect language in tweets prior to 2013). The dataset includes accounts tweeting in a variety of languages over a long period of time. Chinese language tweets appear more often after mid-2017.

This map shows the self-reported locations of the accounts suspended by twitter, color-coded for the language they tweeted in. These locations do not reliably indicate the true location of the account-holder, but in this data set there is a discrepancy between language and location. The self-reported locations are likely to reflect the former nature of the accounts as spam and marketing bots - i.e., they report their locations in developed markets where the consumers they are targeting are located in order to make the accounts appear more credible, even if the true operators of the account are based somewhere else entirely.
Evidence of reselling is clearly present in the dataset. Over 630 tweets within the dataset contain phrases like ‘test new owner’, ‘test’, ‘new own’, etc. As an example, the account @SamanthxBerg tweeted in Indonesian on the 2nd of October 2016, ‘lelang acc f/t 14k/135k via duit. minat? rep aja’ - meaning that the @SamanthxBerg account with 14,000 followers and following 135,000 users, was up for auction. The next tweet on 6th October 2016 reads ‘i just become the new owner, wanna be my friend?.’

tweetid: 782380635990200320
Time stamp: 2016-10-02 00:44:00 UTC
userid: 769790067183190016
User display name: 阿丽木琴
User screen name: SamanthxBerg
Tweet text: PLAYMFS: #ptl lelang acc f/t 14k/135k via duit. minat? rep aja
Use of these kinds of accounts suggests that the operators behind the information operation did not have time to establish the kinds of credible digital assets used in the Russian campaign targeting the US 2016 elections. Building that kind of ‘influence infrastructure’ takes time and the situation in Hong Kong was evolving too rapidly, so it appears that the actors behind this campaign effectively took a short-cut by buying established accounts with many followers.
Timeline of activity
The amount of content directly targeting the Hong Kong protests makes up only a relatively small fraction of the total dataset released by Twitter, comprising just 112 accounts and approximately 1600 tweets, of which the vast majority are in Chinese with a much smaller number in English.
Content relevant to the current crisis in Hong Kong appears to have begun on 14 April 2019, when the account @HKpoliticalnew (profile description: Love Hong Kong, love China. We should pay attention to current policies and people's livelihood. 愛港、愛國,關注時政、民生。) tweeted about the planned amendments to the extradition bill. Tweets in the released dataset mentioning Hong Kong continued at the pace of a few tweets every few days, steadily increasing over April and May, until a significant spike on 14 June, the day of a huge protest in which over a million Hong Kongers (1 in 7) marched in protest against the extradition bill.

Hong Kong related tweets per day from 14 April 2019 to 25 July 2019.
Thereafter, spikes in activity correlate with significant developments in the protests. A major spike occurred on 1 July, the day when protestors stormed the Legislative Council building. This is also the start of the English-language tweets, presumably in response to the growing international interest in the Hong Kong protests. Relevant tweets then appear to have tapered off in this dataset, ending on 25 July.
It is worthwhile noting that the tapering off in this dataset may not reflect the tapering off of the operation itself - instead, it is possible that it reflects a move away from this hastily-constructed information operation to more fully developed digital assets which have not been captured in this data.
Lack of targeted messaging and narratives
One of the features of well-planned information operations is the ability to subtly target specific audiences. By contrast, the information operation targeting the Hong Kong protests is relatively blunt.
Three main narratives emerge:
Condemnation of the protestors
Support for the Hong Kong police and ‘rule of law’
Conspiracy theories about Western involvement in the protests
Support for ‘rule of law’:

tweetid: 1139524030371733504
Time stamp: 2019-06-14 13:24:00 UTC
userid: r+QLQEgpn4eFuN1qhvccxtPRmBJk3+rfO3k9wmPZTQI=
User display name: r+QLQEgpn4eFuN1qhvccxtPRmBJk3+rfO3k9wmPZTQI=
User screen name: r+QLQEgpn4eFuN1qhvccxtPRmBJk3+rfO3k9wmPZTQI=
Tweet text: @uallaoeea 《逃犯条例》的修改,只会让香港的法制更加完备,毕竟法律是维护社会公平正义的基石。不能默认法律的漏洞用来让犯罪分子逃避法律制裁而不管。 - 14 June 2019
Translated: ‘The amendment to the Fugitive Offenders Ordinance will only make Hong Kong's legal system more complete. After all, the law is the cornerstone for safeguarding fairness and justice in society. We can’t allow loopholes in the legal system to allow criminals to escape the arm of the law.’
Conspiracy theories:

tweetid: 1142349485906919424
Time stamp: 2019-06-22 08:31:00 UTC
Userid: 2156741893
User display name: 披荆斩棘
User screen name: saydullos1d
Tweet text: 香港特區警察總部受到包圍和攻擊, 黑衣人嘅真實身份係咩? 係受西方反華勢力指使,然後係背後操縱, 目的明確, 唆使他人參與包圍同遊行示威。把香港特區搞亂, 目的就係非法政治目的, 破環社會秩序。 - 22 June 2019
Translated: ‘Hong Kong SAR police headquarters were surrounded and attacked. Who were the people wearing black? They were acting under the direction of western anti-China forces. They’re manipulating things behind the scenes, with a clear purpose to instigate others to participate in the demonstration and the encirclement. They’re bringing chaos to Hong Kong SAR with an illegal political goal and disrupting the social order.’
[NB: Important to note that this was written in traditional Chinese characters and switches between Standard Chinese and Cantonese, suggesting that the author was a native mandarin speaker but their target audience was Cantonese speakers in Hong Kong.]

tweetid: 1147398800786382848
Time stamp: 2019-07-06 06:56:00 UTC
Userid: 886933306599776257
User display name: lingmoms
User screen name: lingmoms
Tweet text: 無底線的自由,絕不是幸事;不講法治的民主,只能帶來禍亂。香港雖有不錯的家底,但經不起折騰,經不起內耗,惡意製造對立對抗,只會斷送香港前途。法治是香港的核心價值,嚴懲違法行為,是對法治最好的維護,認為太平山下應享太平。 - 6 July 2019
Translated: ‘Freedom without a bottom line is by no means a blessing; democracy without the rule of law can only bring disaster and chaos. Although Hong Kong has a good financial background, it can’t afford to vacillate. It can’t take all of this internal friction and maliciously created agitation, which will only ruin Hong Kong's future. The rule of law is the core value of Hong Kong. Severe punishment for illegal acts is the best safeguard for the rule of law. Peace should be enjoyed at the foot of The Peak.’’
[NB: This Tweet is also written in Standard Chinese using traditional Chinese characters. The original text says ‘at the foot of Taiping mountain’, meaning Victoria Peak, but is more commonly referred to in Hong Kong as "The Peak" (山頂). However, the use of Taiping mountain instead of ‘The Peak’ to refer to the feature is a deliberate pun, because Taiping means ‘great peace’]

tweetid: 1152024329325957120
Time stamp: 2019-07-19 01:16:00 UTC
Userid: 58615166
User display name: 流金岁月
User screen name: Licuwangxiaoyua
Tweet text: #HongKong #HK #香港 #逃犯条例 #游行 古话说的好,听其言而观其行。看看那些反对派和港独分子,除了煽动上街游行、暴力冲击、袭警、扰乱香港社会秩序之外,就没做过什么实质性有利于香港发展的事情。反对派和港独孕育的“变态游行”这个怪胎,在暴力宣泄这条邪路上愈演愈烈。 - 19 July 2019
Translated: ‘#HongKong #HK #HongKong #FugitiveOffendersOrdinance #Protests The old Chinese saying put it well: ‘Judge a person by their words, as well as their actions’. Take a look at those in the opposition parties and the Hong Kong independence extremists. Apart from instigating street demonstrations, violent attacks, assaulting police officers and disturbing the social order in Hong Kong, they have done nothing that is actually conducive to the development of Hong Kong. This abnormal fetus of a “freak demonstration” that the opposition parties and Hong Kong independence people gave birth to is becoming more violent as it heads down this evil road.’
This approach of vilifying opponents, emphasising the need for law and order as a justification for authoritarian behaviour is consistent with the narrative approaches adopted in earlier information operations contained within the dataset (see below).
Earlier information operations against political opponents
Our research has uncovered evidence that the accounts identified by Twitter were also engaged in earlier information campaigns targeting opponents of the Chinese government.
It appears likely that these information operations were intended to influence the opinions of overseas Chinese diasporas, perhaps in an attempt to undermine critical coverage in Western media of issues of interest to the Chinese government. This is supported by a notice released by China News Service, a Chinese-language media company owned by the United Front Work Department that targets the Chinese diaspora, requesting tenders to expand its Twitter reach.
Campaign against Guo Wengui
The most significant and sustained of these earlier information operations targets Guo Wengui, an exiled Chinese businessman who now resides in the United States. The campaign directed at Guo is by far the most extensive campaign in the dataset and is significantly larger than the activity directed at the Hong Kong protests. This is the earliest activity the report authors have identified that aligns with PRC interests.
Graph showing activity in an information operation targeting Guo from 2017 to the end of the dataset in July 2019
Guo, aso known as Miles Kwok, fled to the United States in 2017 following the arrest of one of his associates, former Ministry of State Security vice minister Ma Jian. Guo has made highly public allegations of corruption against senior members of the Chinese government. The Chinese government in turn accused Guo of corruption, prompting an Interpol red notice for his arrest and return to China. Guo has become a vocal opponent of the Chinese government, despite having himself been accused of spying on their behalf in July 2019.
Within the Twitter Hong Kong dataset, the online information campaign targeting Guo began on 24 April 2017, five days after the Interpol red notice was issued at the request of the Chinese government, and continued until the end of July 2019. Guo continues to be targeted on Twitter, although it is unclear if the PRC government is directly involved in the ongoing effort.

Tweets mentioning Guo Wengui over time from 23 April 2017 to 4 May 2017: Graph showing activity in tweet volume by day. Activity appears to take place during the working week (except Wednesdays), suggesting that this activity may be professional rather than authentic personal social media use.
In total, our research identified at least 38,732 tweets from 618 accounts in the dataset which directly targeted Guo. These tweets consist largely of vitriolic attacks on his character, ranging from highly personal criticisms to accusations of criminality, treachery against China and criticisms of his relationship with controversial US political figure Steve Bannon.

tweetid: 1123765841919660032
Time stamp: 2019-05-02 01:47:00 UTC
Userid: 4752742142
User display name: 漂泊一生
User screen name: futuretopic
Tweet text: “郭文贵用钱收买班农,一方面想找靠山,一方面想继续为自己的骗子生涯增加点砝码,其实班农只是爱财并非真想和郭文贵做什么, 很快双方会发现对方都 是在欺骗自己,那时必将反目成 仇.” - 2 May 2019
Translated: “Guo Wengui used his money to buy Bannon. On the one hand, he needed his backing. On the other hand, he wanted to continue to add weight to his career as a swindler. In fact, Bannon just loves money and doesn't really want to do anything with Guo Wengui. Soon both sides will find out that they're both deceiving the other, and then they'll turn into enemies.”

tweetid: 1153122108655861760
Time stamp: 2019-07-22 01:58:00 UTC
Userid: 1368044863
User display name: asdwyzkexa
User screen name: asdwyzkexa
Tweet text: ‘近日的郭文贵继续自己自欺欺人的把戏,疯狂的直播,疯狂的欺骗,疯狂鼓动煽风点火,疯狂的鼓吹自己所谓的民主,鼓吹自己的“爆料革命”。但其越是疯狂,越是难掩日暮西山之态,无论其吹的再如何天花乱坠,也终要为自己的过往负责,亲自画上句点.’ - 22 July 2019
Translated: ‘Lately, Guo Wengui has continued to use his cheap trick of deceiving himself and others with a crazy live-stream where he lied like crazy, incited and fanned the flames like crazy, and agitated for his so-called democracy like crazy—enthusiastically promoting his "Expose Revolution". But the crazier he gets the harder it is to hide the fact that the sun has already set on him. It doesn't matter how much he embellishes things; eventually, he will have to take responsibility and put an end to all of this himself.'
Spikes in activity in this campaign appear to correspond with significant developments in the timeline of Guo’s falling out with the Chinese government. For example, a spike around 23 April 2018 (see below chart) correlates with the publishing of a report by the New York Times exposing a complex plan to pull Guo back to China with the assistance of the United Arab Emirates and Trump fundraiser Elliott Broidy.

tweetid: 988088232075083776
Time stamp: 2018-04-22 16:12:00 UTC
Userid: 908589031944081408
User display name: 如果
User screen name: bagaudinzhigj
Tweet text: ‘‘谎言说一千遍仍是谎言,郭文贵纵有巧舌如簧的口才,也有录制性爱视频等污蔑他人的手段,更有给人设套录制音频威胁他人的前科,还有诈骗他人钱财的146项民事诉讼和19项刑事犯罪指控,但您在美国再卖力的表演也掩盖不了事实.’ - 22nd April 2018
Translated: ‘Even if a lie is repeated a thousand times, it's still a lie. Guo Wengui is an eloquent smooth talker and uses sex tapes and other methods to slander people. He also has a criminal record for trying to threaten and set people up with recorded audio. He has 146 civil lawsuits and 19 criminal charges for swindling other people's money. No matter how much effort you put in in the United States, you still can't hide the truth.’
This tweet was repeated 41 times by this user from 7 November 2017 to 15 June 2018, at varying hours of the day, but at only 12 or 42 minutes past the hour, suggesting an automated or pre-scheduled process:


Volume of tweets mentioning Guo Wengui over time from 14 April 2019 to 29 April 2019.
Like the information operation targeting the Hong Kong protests, the campaign targeting Guo is primarily in Chinese language. There are approximately 133 tweets in English, many of which are retweets or duplicates. On 5th November 2017, for example, 27 accounts in the dataset tweeted or retweeted: ‘#郭文贵 #RepatriateKwok、#Antiasylumabused、 sooner or later, your fake mask will be revealed.’
As the Hong Kong protests began to increase in size and significance, the information operations against Guo and the protests began to cross over, with some accounts directing tweets at both Guo and the protests.

tweetid: 1148407166920876032
Time stamp: 2019-07-09 01:42:00 UTC
Userid: 886933306599776257
User display name: lingmoms
User screen name: lingmoms
Tweet text: ‘唯恐天下不乱、企图颠覆香港的郭文贵不仅暗中支持香港占中分子搞暴力破坏,还公开支持暴力游行示威,难道这一小撮入狱的暴民就是文贵口中的“香港人”?’- 9 July 2019
Translated: ‘Guo Wengui, who fears only a world not in chaos and schemes to toppleHong Kong, is not only secretly supporting the violent and destructive Occupy extremists in Hong Kong, he's also openly supporting violent demonstrations. Is this small mob of criminals the "Hong Kong people" Guo Wengui keeps talking about?’
The dataset provided by Twitter ends in late July 2019, but all indications suggest that the information campaign targeting Guo will continue.
Campaign against Gui Minhai
Although the campaign targeting Guo Wengui is by far the most extensive in the dataset, other individuals have also been targeted.
One is Gui Minhai, a Chinese-born Swedish citizen. Gui is one of a number of Hong Kong-based publishers specialising in books about China’s political elite who disappeared under mysterious circumstances in 2015. It was later revealed that he had been taken into Chinese police custody. The official reason for his detention is his role in a fatal traffic accident in 2003 in which a schoolgirl was killed. Gui has been in and out of detention since 2015, and has made a number of televised confessions which many human rights advocates believe to have been forced by the Chinese government.
The information operation targeting Gui Minhai is relatively small, involving 193 accounts and at least 350 tweets. With some exceptions, the accounts used in the activity directed against Gui appear to be primarily ‘clean’ accounts created specifically for use in information operations, unlike the repurposed spam accounts utilised by the activity targeted at Hong Kong.
The campaign runs for one month, from 23 January to 23 February 2018. The preciseness of the timing is indicative of an organised campaign rather than authentic social media activity. The posting activity also largely corresponds with the working week, with breaks for weekends and holidays like Chinese New Year.

A graph showing campaign activity in tweets per day. Weekends and public holidays are indicated by grey shading.
The campaign started on 23 January 2018, the day on which news broke that Chinese police had seized Gui off a Beijing-bound train while he was travelling with Swedish diplomats to their embassy. The campaign then continued at a slower pace across several weeks, ending on 23 February 2018. The tweets are entirely in Chinese language and emphasise Gui’s role in the traffic accident, painting him as a coward for attempting to leave the country and blaming Western media for interfering in the Chinese criminal justice process. Some also used Gui’s name as a hashtag.

tweetid: 956700365289807872
Time stamp: 2018-01-26 01:28:00 UTC
Userid: 930592773668945920
User display name: 赵祥
User screen name: JonesJones4780
Tweet text: ‘#桂民海 因为自己一次醉驾,让一个幸福家庭瞬间支离破碎,这令桂敏海痛悔不已。但是,他更担心自己真的因此入狱服刑。于是,在法院判决后不久、民事赔偿还未全部执行完的时候,桂敏海做出了另一个错误选择.’ - 26 January 2018
Translation: ‘#GuiMinhai deeply regrets that a happy family was shattered because of his drunk driving. However, he’s even more worried that he’s actually going to have to serve a prison sentence for it. Therefore, not long after the court’s decision and before any civil compensation was paid out, Gui Minhai made another bad choice’

tweetid: 956411588386279424
Time stamp: 2018-01-25 06:21:00 UTC
Userid: 1454274516
User display name: 熏君
User screen name: nkisomekusua
Tweet data: ‘#桂敏海 西方舆论力量仍想运用它们的话语霸权和双重标准,控制有关中国各种敏感信息的价值判断,延续对中国政治体制的舆论攻击,不过西方媒体这样的炒作都只是自导自演,自娱自乐.’ - 25 January 2018
No comments:
Post a Comment