Sep 14, 2015
During the Cold War the United States military misplaced at least eight nuclear weapons permanently. These are the stories of what the Department of Defense calls “broken arrows”—America’s stray nukes, with a combined explosive force 2,200 times the Hiroshima bomb.
February 13, 1950. An American B-36 bomber en route from Alaska to Texas during a training exercise lost power in three engines and began losing altitude. To lighten the aircraft the crew jettisoned its cargo, a 30-kiloton Mark 4 (Fat Man) nuclear bomb, into the Pacific Ocean. The conventional explosives detonated on impact, producing a flash and a shockwave. The bomb’s uranium components were lost and never recovered. According to the USAF, the plutonium core wasn’t present.
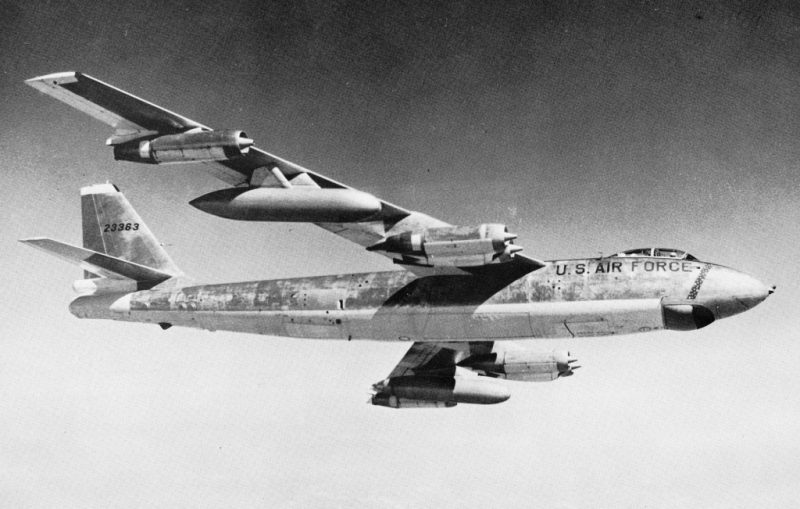
March 10, 1956. A B-47 carrying two nuclear weapon cores from MacDill Air Force Base in Florida to an overseas airbase disappeared during a scheduled air-to-air refueling over the Mediterranean Sea. After becoming lost in a thick cloud bank at 14,500 feet, the plane was never heard from again and its wreckage, including the nuclear cores, was never found. Although the weapon type remains undisclosed, Mark 15 thermonuclear bombs (commonly carried by B-47s) would have had a combined yield of 3.4 megatons.
You might also like


No comments:
Post a Comment